|^·<×>·v| |
1 |
Abstract
|
1 |
|
Introduction |
This study complements
the customary statistical homogeneity analyses
(i. e. the computations of the achievable variance reduction
and the remaining dispersion within DRGs)
by means of a comparison of DRG systems on the level of base DRGs.
|
2 |
|
Data |
The study is based on 900,000 records from Swiss hospitals from
the years 2000 to 2003.
The records were selected according to quality criteria.
|
3 |
|
Method |
Pair comparisons were conducted to try to compute the
divergence in the assignment of base DRGs of the AP-DRG,
APR-DRG, AR-DRG, IR-DRG systems among each other, and
for individual evaluations also according to SQLape, LDF
and CCS, and to represent the results graphically. For
this purpose, a so-called "fractionation coefficient"
was developed.
Visualisation was effected on the basis of treemaps.
|
4 |
|
Results |
The study yielded the following results: the actual DRG
systems (AP, APR, AR, IR) partially display similar grouping
concepts in the medical sphere.
In this respect, the greatest similarities exist between AP and APR,
and between IR and APR.
In the surgical sphere, AP and, to a lesser extent, AR
were found to have some common features with APR;
apart from this, it became apparent that the surgical base DRGs
are more diverse in their make-up than medical base DRGs.
The most conspicuous differences were discovered between
the surgical base IR DRGs and the surgical base DRGs
of the other DRG systems.
|
5 |
|
|
In order to be able to compare the SQLape categories with the
base DRGs in spite of the differing construction approach,
the SQLape code of the main treatment was established for each
individual hospital case. In addition, some analyses were also
conducted with the help of the primary SQLape codes computed
by the manufacturer. Correspondence with the other systems
was relatively low. However, the different perspective also
can serve to detect deficiencies in the DRG systems.
|
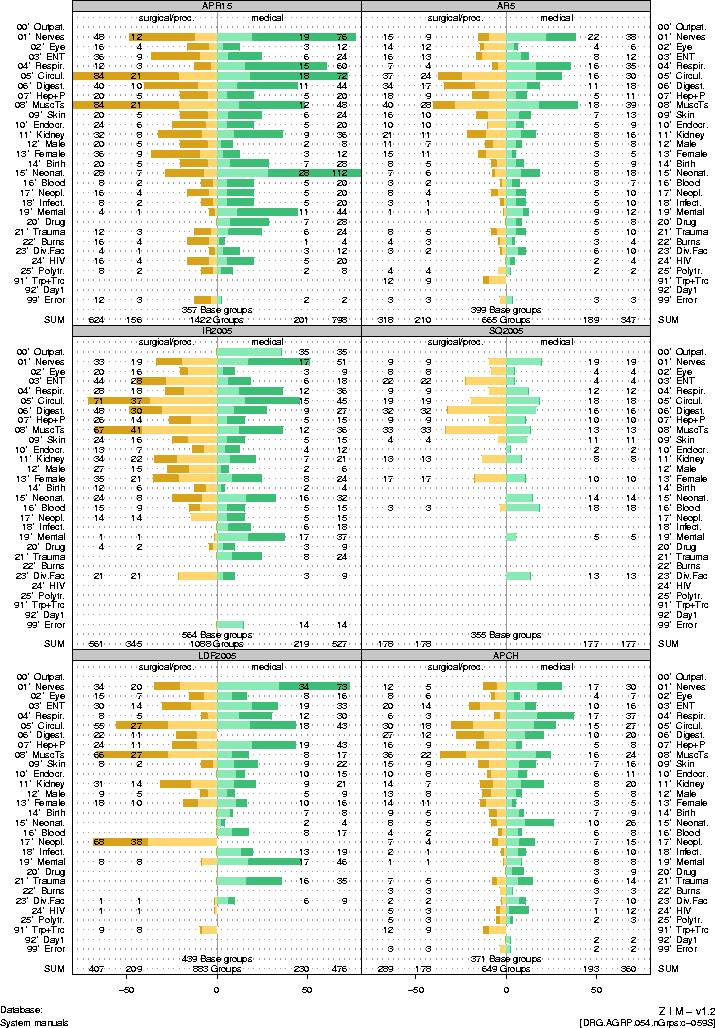
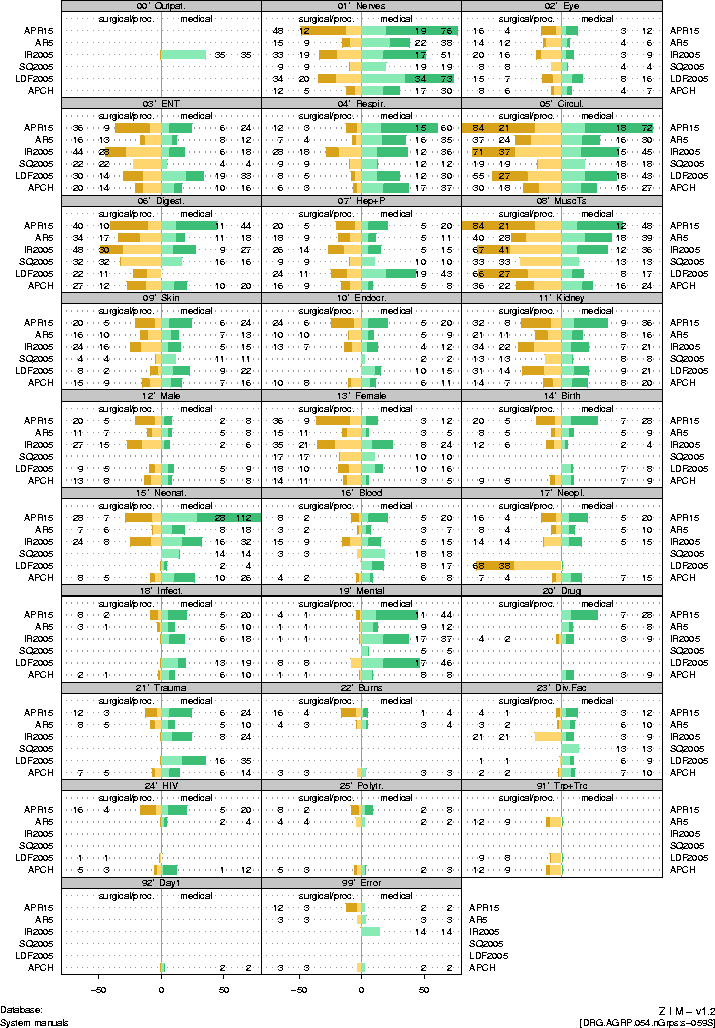
6 |
|
|
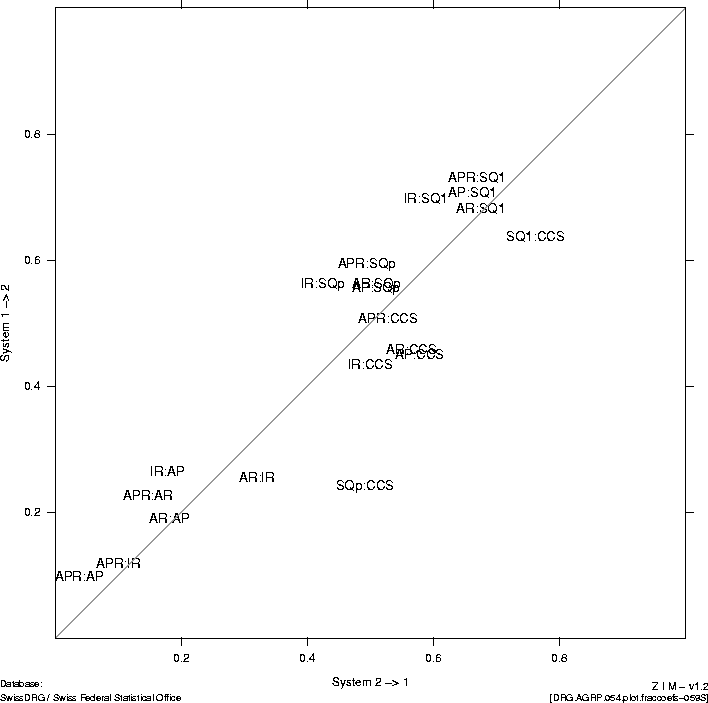
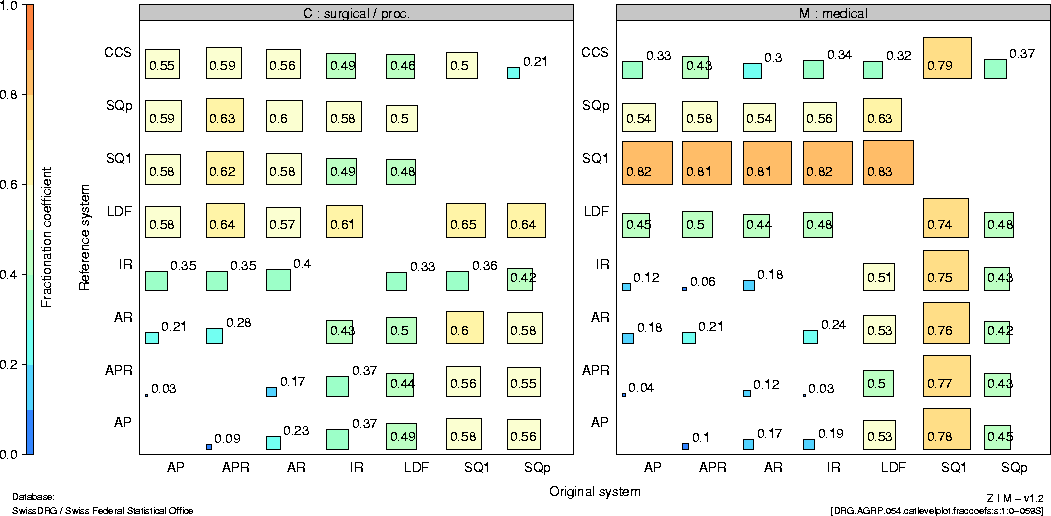
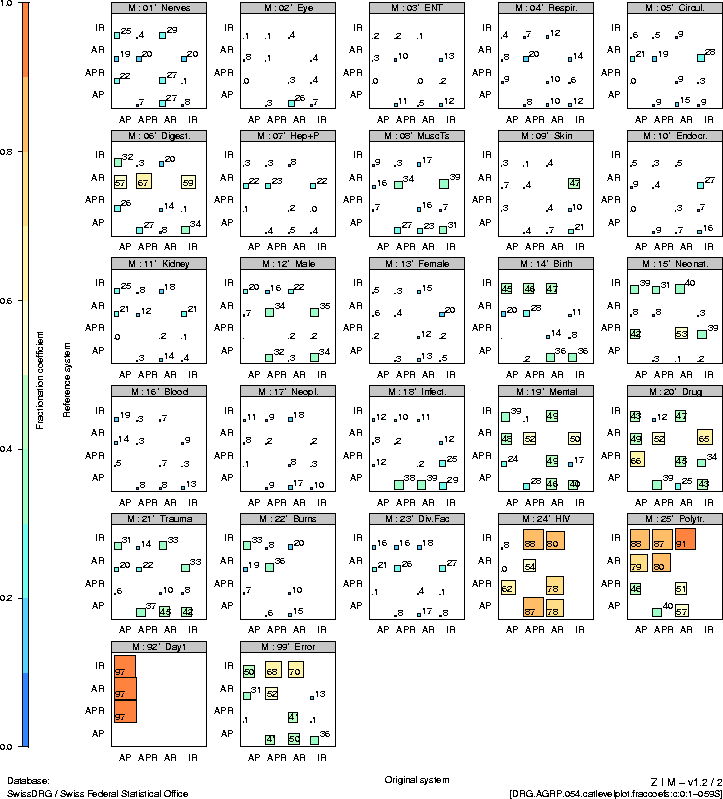
In comparison with the CCS classification, which is also
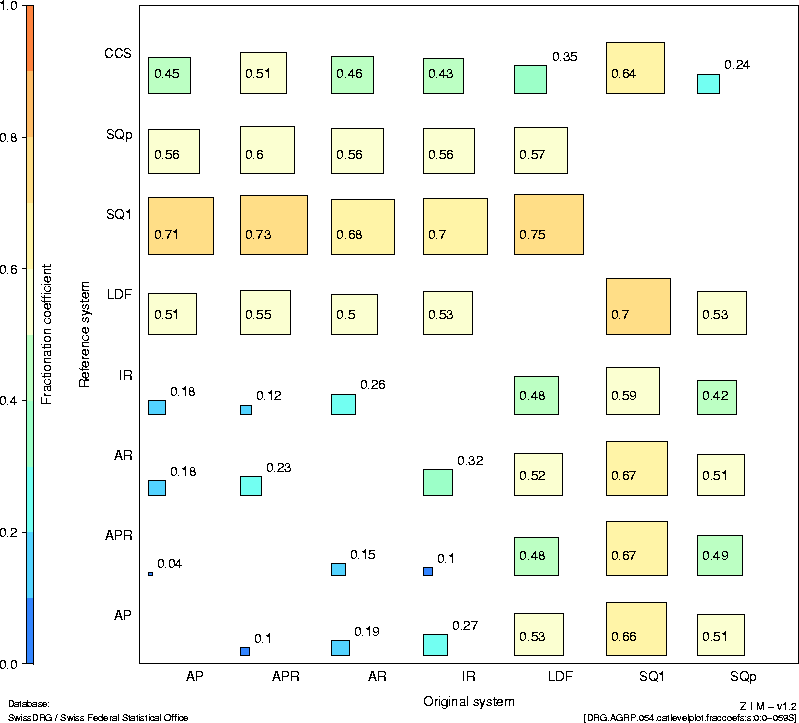
based on a diverging concept, all the systems showed great
differences,
with the surgical SQLape main treatment categories
being the exception.
|
7 |
|
Conclusions |
The definitions of a great number of base DRGs are
distinctly different in the systems under scrutiny.
With regard to the choice of a DRG system, this means that it
is not merely a licenser and a cooperation model that are chosen,
but at the same time also a certain way of viewing clinical treatment.
|
8 |
|
|
|
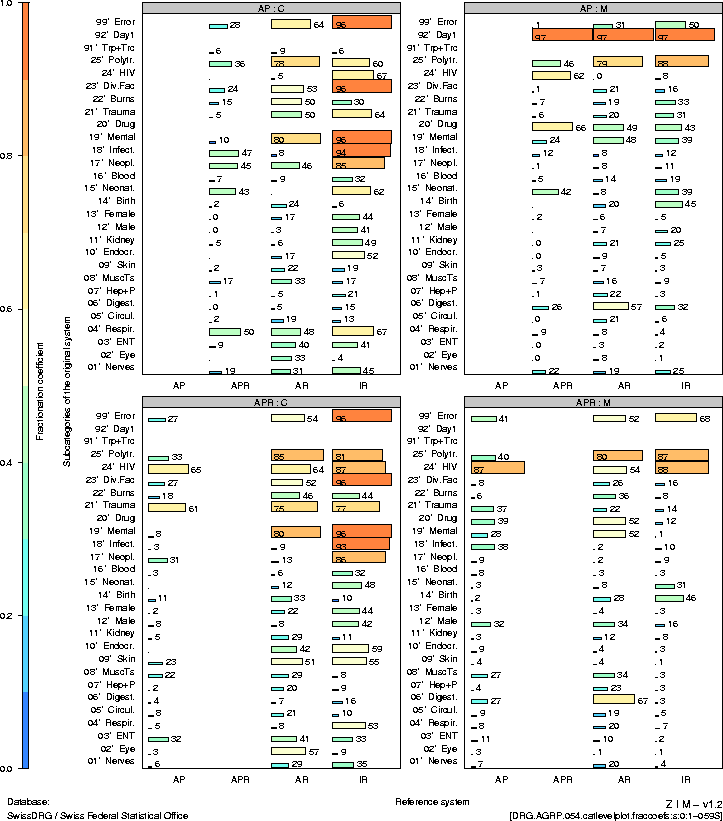
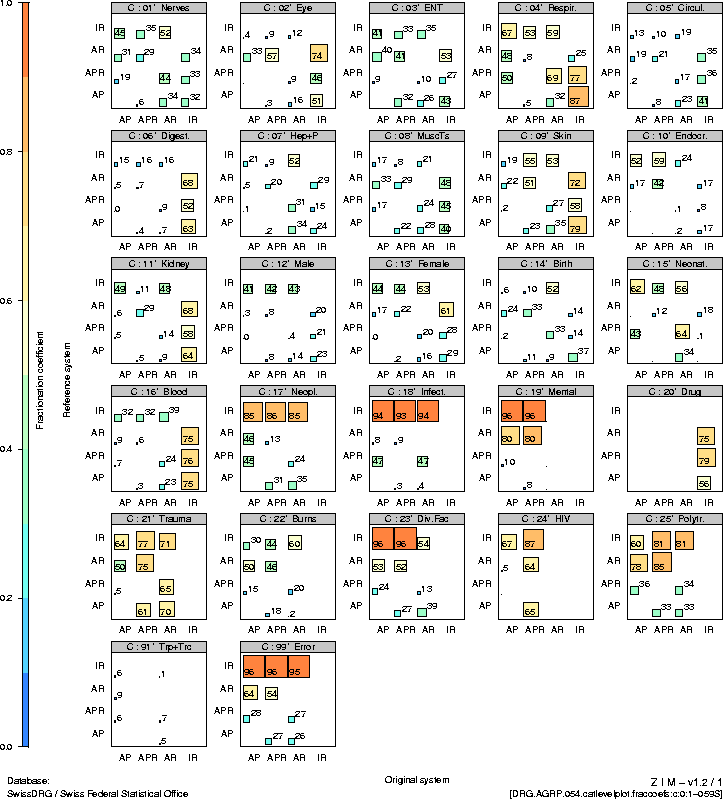
|
|^·<×>·v| |
2 |
Introduction
|
9 |
|^·<×>·v| |
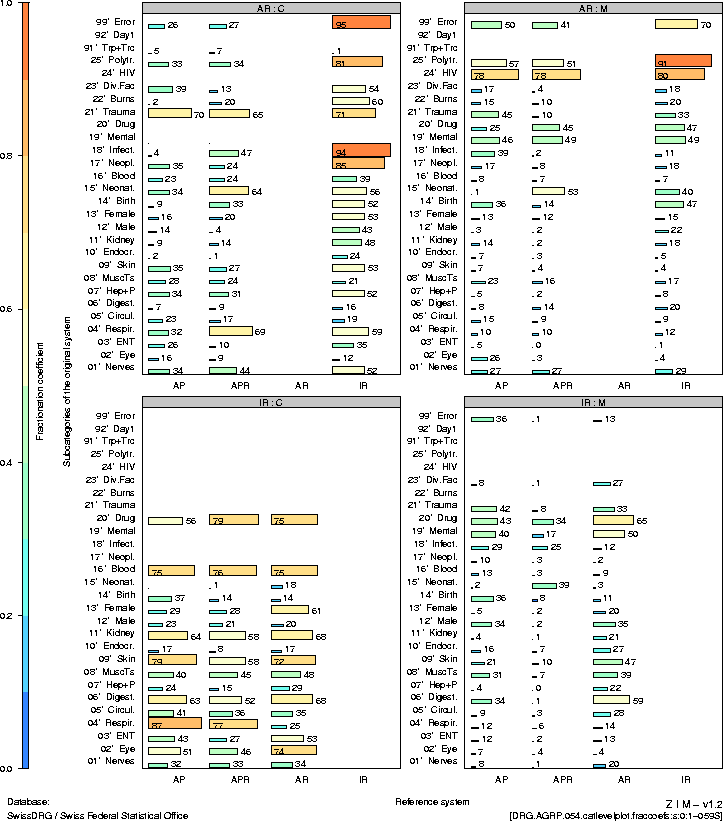
2.1 |
Starting point
|
10 |
1
http:// www.swissdrg.org /.
2
http:// www.swissdrg.org /.
|
A DRG system for Switzerland |
One of the tasks of the SwissDRG project1
is to select a national DRG system for Switzerland.
It is to be expected that the first step will consist in making an
existing system compatible with the coding systems used in
Switzerland. Subsequently, the system will be subjected to
adaptation and corrections with a view to making it usable
in Switzerland.
|
11 |
|
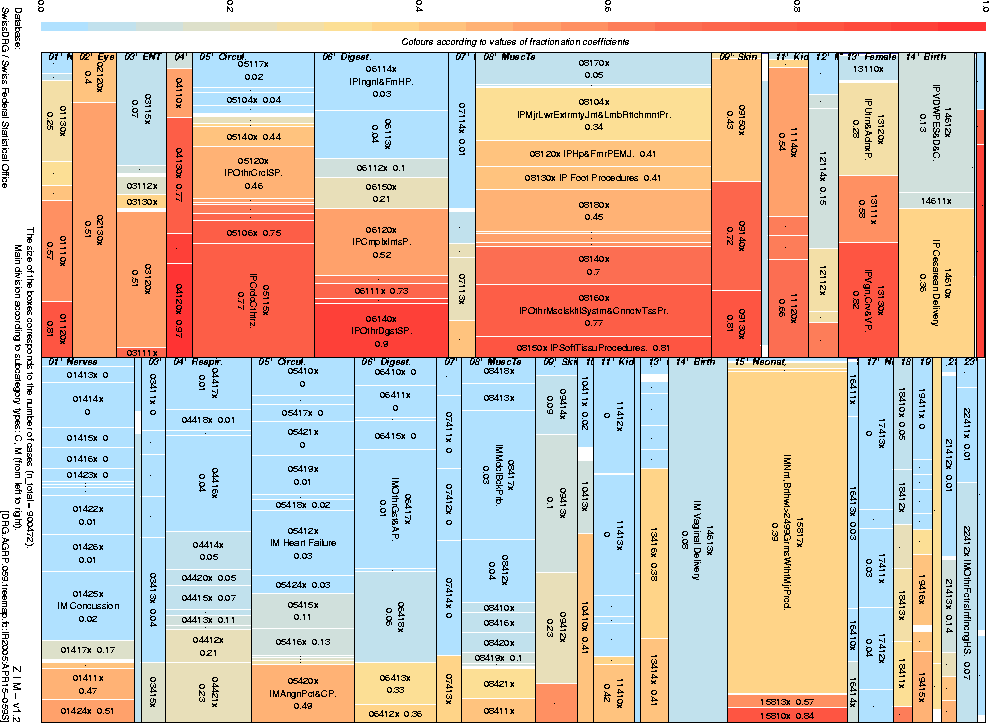
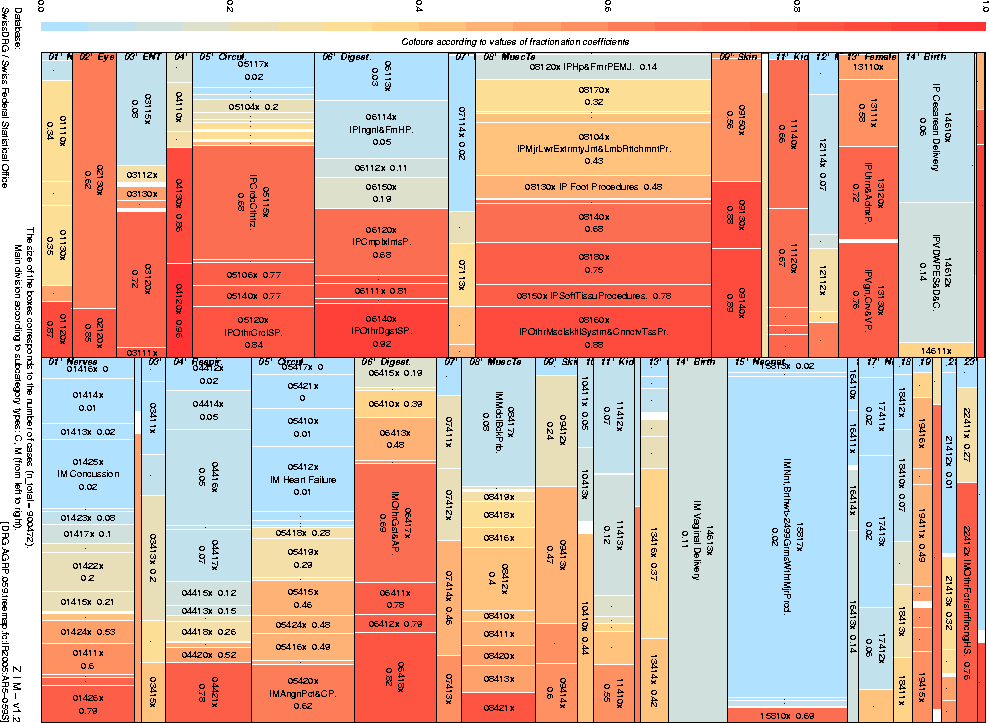
System assessment |
It is necessary that both the selection of, and any later
modifications to, such a system should be based not only
on economic calculations but also on substantial clinical analyses.
|
12 |
3
Fischer [Basis-DRG-Vergleiche, 2005].
4
Fischer [Basis-DRG-Vergleiche, 2005].
|
Commission |
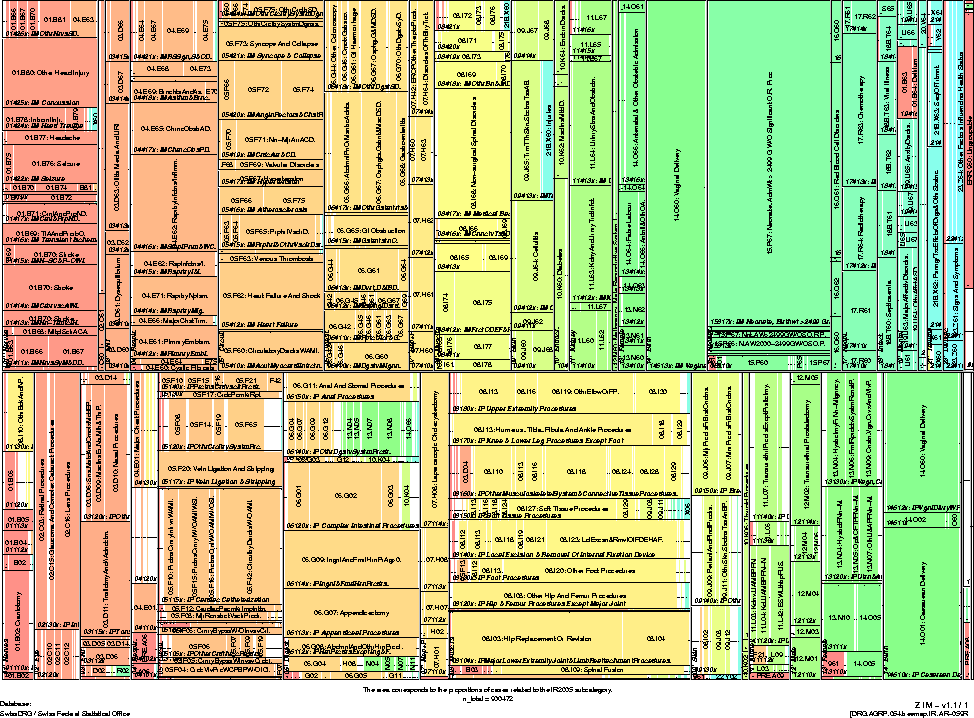
In view of the system selection, SwissDRG commissioned the
Zentrum für Informatik und wirtschaftliche Medizin (ZIM)
to compare selected DRG systems (APR-DRG, AR-DRG, IR-DRG;
SQLape) on the basis of the base DRGs. The study thus conducted
was then extended by ZIM.2
This paper presents the state of the work done to date.
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
2.2 |
Relative clinical homogeneity
|
14 |
|
Economic homogeneity |
Examinations of DRG systems usually apply statistical
homogeneity analyses, such as the computation of variance
reduction in respect of length of stay or of costs, or the
calculation of the remaining dispersion of these variables
within DRGs. Calculations of this type serve to examine
economic homogeneity: the dependent variable that is meant
to be explained by the DRG classification is a variable
that can be or has been valued in monetary terms. A DRG is
economically homogeneous if the costs of the cases assigned
to this DRG are similar.
|
15 |
|
Clinical homogeneity |
The assessment of clinical homogeneity focuses on the question
as to whether syndromes and/or treatments of patients that are
assigned to the same DRG, are similar. This question is less
easy to answer by means of statistical methods. The measure
of correspondence between existing diagnosis and/or procedure
codes might be able to provide a pointer but will remain
unreliable since some codes differentiate more strongly than
others and also since hospital cases of a similar type may be
represented equally correctly with differing code combinations.
|
16 |
|
Relative clinical homogeneity |
As a way out of this situation, an attempt was now made, not
to assess clinical homogeneity as such, but to compare the
classification of hospital cases in different DRG systems
with each other. The more concordant the concentration of
hospital cases in individual DRGs, the greater the
"relative clinical homogeneity".
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
3 |
Data
|
18 |
|^·<×>·v| |
3.1 |
DRG systems taken into account
|
19 |
5
Cf. Fischer [PCS, 1997].
6
Vgl. Fischer [PCS, 1997];
Fischer [DRG-Systeme, 2000].
7
APDRG-CH [CW 4.1, 2003];
3M [AP-DRG-CH, 1998].
8
http:// solutions.3m.com / wps / portal / 3M / en _ US / 3M _ Health _ Information _ Systems / HIS / Products / APRDRG _ Software /.
9
http:// www.health.gov.au / internet / main / publishing.nsf / Content / health-casemix-ardrg1.htm.
10
Cf. Mullin et al. [IR-DRG, 2002].
|
DRG systems |
The following DRG systems3 were examined:
-
APDRG-CH:
All Patient Diagnosis Related Groups
(Hersteller: 3M, USA).4
- APR-DRG-15:
All Patient Refined Diagnosis Related Groups (3M, USA).5
- ARDRG-5:
Australian Refined Diagnosis Related Groups (Australien).6
- IRDRG-2005:
International Refined Diagnosis Related Groups (3M, USA).7
|
20 |
11
http:// www.sqlape.com /.
12
BMGF-A [LKF05-Modell, 2004];
http:// www.bmg.gv.at / home / Schwerpunkte / Krankenanstalten /.
13
http:// www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov / toolssoftware / icd _ 10 / ccs _ icd _ 10.jsp.
Vgl. auch Zahnd [CCS, 2004];
Zahnd [CCS, 2003].
|
Additional systems |
In a number of evaluations, the following
patient classification systems were used
as additional reference systems:
- SQLape 2005:
Striving for Quality Level and Analysis of Patient Expenditures (Sqlape, Schweiz).8
- LDF 2005:
Leistungsbezogene Diagnosen-Fallgruppen (Österreich).9
- CCS:
Clinical Classification Software (USA).10
|
21 |
|
Multiple SQLape categories
per case
|
Compared to the established DRG systems,
the SQLape system uses a different classification concept.
As in DRG systems, only one cost weight results
for each hospital stay.
Yet the SQLape system functions with a number of patient groups
which is clearly lower than the number of DRGs in DRG systems,
that is to say with only about 350 SQLape categories
compared with 640 to more than 1200 DRGs.
This is possible because only treatments and diseases are
represented by SQLape categories
but not severity degrees.
Instead of severity categories (e. g. DRGs with or without CC)
more than one SQLape category can be assigned to one hospital stay.
Furthermore, the main diagnosis does not decide
the attribution of a primary patient category,
but it is used the same way as all secondary diagnoses.
|
22 |
|
"Primary" SQLape categories
|
If a hospital case is assigned to several SQLape categories,
the system marks
the first group assigned following the the grouping hierarchy
as "primary" SQLape category.
|
23 |
|
Grouping |
The hospital cases in the database were grouped
according to the mentioned patient classification systems
by Hervé Guillain and Dung Duong of the
CHUV (Centre hospitalier universitaire vaudois, Lausanne).
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
3.2 |
Database
|
25 |
14
http:// www.apdrgsuisse.ch /.
15
http:// www.swissdrg.org /.
16
http:// www.apdrgsuisse.ch /
17
http:// www.swissdrg.org /
|
Data base |
[Table 1]
The database that was used contains just over 900,000 cases
from the years 2000 to 2003.
There are data from the
Swiss APDRG Association11 as well as the data sets additionally made available
to the SwissDRG project12 by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office (SFSO).
|
26 |
Table 1:
Data according to years and hospital types
|
| Hospital type
| 2000
| 2001
| 2002
| 2003
| SUMME
| in %
|
| From APDRG-CH survey
| 70319
| 56949
| 68593
|
| 195861
| 21.75
|
| K111 University hospitals
|
|
| 89971
| 95417
| 185388
| 20.59
|
| K112 Central hospitals
|
|
| 84790
| 87744
| 172534
| 19.16
|
| K121 Regional hospitals level 3
|
|
| 68738
| 81796
| 150534
| 16.72
|
| K122 Regional hospitals level 4
|
|
| 76776
| 87833
| 164609
| 18.28
|
| K123 Regional hospitals level 5
|
|
| 12705
| 12928
| 25633
| 2.85
|
| K232 Special gyn./neonat. clinics
|
|
| 2874
| 3039
| 5913
| 0.66
|
| sum
| 70319
| 56949
| 404447
| 368757
| 900472
| 100.00
|
| in %
| 7.81
| 6.32
| 44.92
| 40.95
| 100.00
|
|
27 |
|
APDRG-CH data |
The data from the Swiss APDRG Association
come from the hospitals of
the CHUV and individual hospitals in the Cantons of Ticino,
Valais and Neuchâtel from the years 2000 to 2003.
|
28 |
18
BFS-CH [Medizinische Statistik, 1997].
19
These quality indicators are described in
Schwab/Meister [CMI, 2004]: 15.
20
BFS-CH [Medizinische Statistik, 1997].
21
Diese Qualitätsindikatoren sind beschrieben in
Schwab/Meister [CMI, 2004]: 15.
|
SFSO data
Quality criteria
|
The SFSO data come from hospitals all over Switzerland from the
years 2002 and 2003, with the SFSO selecting the data of those
hospitals in the survey of medical statistics13
which satisfied the following quality criteria:14
-
The case figures between medical and administrative
statistics differ by no more than 5 %.
-
More than an average of 2.2 diagnoses per case are available.
|
29 |
|
|
The number of hospitals involved cannot
be detected from the data supplied.
|
30 |
22
In Switzerland, length of stay is calculated by
counting both the day of admission and the day of discharge.
23
Bei der Berechnung der Aufenthaltsdauer
wird in der Schweiz
sowohl der Eintrittstag wie auch der Austrittstag gezählt.
|
|
The mean length of stay was 8.2 days.
The median was located at 6 days,
the first quartile at 3,
the third quartile at 10 days.15
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
24
According to an e-mail from Hervé Guillain, CHUV,
dated 20 April 2005.
25
Gemäss E-Post von Hervé Guillain, CHUV, vom 20.4.2005.
|
Selection of the main procedure |
In the SFSO data, the main procedure was already encoded as such.
Since this was not the case with the data from
the Swiss APDRG Association,
Guillain and Doung from the CHUV determined the
hospital cases for the main procedure as follows:16
-
That code was selected from among the procedure codes
which would be recognised as an surgical code by the AP-DRG grouper
and which influences DRG assignment.
-
Failing that, that code was selected from the procedure codes
which influences DRG assignment.
-
Failing that, that code was selected from the procedure codes
which would be recognised as an surgical code by the AP-DRG grouper.
-
Failing that, the first existing procedure code was selected.
|
32 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
4 |
Methods
|
33 |
|^·<×>·v| |
4.1 |
The Definition of "base DRGs"
|
34 |
26
Fischer [DRG-Systeme, 2000]: 27, on the basis
of the "adjacent DRGs" ("ADRGs")
defined in the RDRG and APR-DRG systems.
–
Cf. Freeman JL et al. [1991]: 63 ff.
27
Fischer [DRG-Systeme, 2000]: 27,
aufgrund der im RDRG- und im APR-DRG-System
definierten "adjacent-DRGs" ("ADRGs").
–
Vgl. Freeman JL et al. [1991]: 63 ff.
|
|
Base DRGs (base groups, adjacent DRGs)
result from the combination of the adjacent DRGs without splits
by complications and comorbidities and/or age groups.17
|
35 |
|
Proposed definition |
The following definition would be more differentiated: in a
DRG system, those patient groups are labelled "base DRGs"
which can be distinguished according to main diagnoses and procedures
but not according to any of the following split criteria:
-
CC (comorbidities and complications).
-
Age.
-
Type "complicating diagnosis".
-
Type "complicating procedure".
-
With/without death during hospital stay.
-
Reason for discharge: against medical advice.
-
Transfer within a given period of time.
-
Possibly certain procedures
(such as APDRG 411/422 with/without endoscopy).
-
AP-MDC 15: possibly birth weight and/or significant procedures.
-
AP-MDC 24: possibly with/without tuberculosis (DRGs for HIV patients).
-
AP-MDC 24: possibly type of associated diagnoses.
|
36 |
28
Cf. among others the example in
Roeder et al. [G-DRGs 2005 Teil 2, 2004]: 1022 f.
29
Vgl. u. a. das Beispiel in
Roeder et al. [G-DRGs 2005 Teil 2, 2004]: 1022 f.
30
AP-DRG: Fischer [DRG+Pflege, 2002]: 327–367.
AR-DRG: Fischer [DRG+Pflege, 2002]: 368–423.
|
|
Annotations:
-
In the AR-DRG system,
the base DRGs are known and can be encoded.
(The first three characters of the code designate the base AR-DRG.)
In the
RDRG,
APR-DRG,
IR-DRG,
LDF,
EfP (from GHM),
as well as in SQLape, the base DRGs are also designated and encoded.
In these systems, it would have to be examined whether and to what extent
the predefined base DRGs fit the above definition.
-
In the G-DRG system 2005,
the concept of base DRGs initially taken over from the AR-DRG system
was broken up for the purpose of avoiding a conflict with procedure
hierarchy.18
The base GDRGs can still be determined;
however, this is no longer done on the strength of the G-DRG codes
but on the basis of an analysis of the G-DRG label.
-
Draft lists of APDRGs and base ARDRGs can be found in
Fischer [DRG+Pflege, 2002].19
|
37 |
|
For this study: adoption of the manufacturers'
base DRG definitions
|
With one single exception, the DRG systems analysed in this study
already had base groups labelled by the manufacturer.
For financial reasons, these base groups were adopted
without any further analysis.
|
38 |
|
|
Only the AP-DRG system was not equipped with a labelled
list of base groups. For the determination of the
base APDRGs, the data were only grouped according to main
diagnosis and main procedure. To identify the base APDRGs,
the AP-DRG codes were preceded by an "A-"
(for "adjacent").
|
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
Determination of the SQLape category of the main treatment:
"SQp" |
In order to be able to conduct
1:1 comparisons between SQLape categories and DRGs,
the SQLape procedure category
that the system returned when only the main
diagnosis and the main procedure were grouped,
was used as the base group;
if no SQLape procedure category existed,
use was made of the
SQLape diagnosis category returned.
This patient category was called
"SQLape main treatment category".
The abbreviation "SQp" was used.
|
40 |
31
In the data used, 18.7 % of the hospital cases
were grouped with more than one SQLape category:
13.4 % of the cases were encoded with two SQLape categories,
3.1 % with three,
and the remaining 1.1 % with more than three.
32
Bei den verwendeten Daten wurden 18.7 % der Behandlungsfälle
mit mehr als einer SQLape-Kategorie gruppiert:
13.4 % der Fälle waren mit zwei, 3.1 % mit drei
und der Rest von 1.1 % mit mehr als drei SQLape-Kategorien codiert.
|
Primary SQLape category:
"SQ1" |
In the course of the work done on the study, the manufacturer
defined the first SQLape category as the primary SQLape
category, which also increased comparability with DRG systems.
It must be borne in mind, however, that in approximately 20 %
of all hospital cases20,
further SQLape categories
are assigned besides this primary SQLape category.
(DRG systems utilise a ranking according to degrees of severity
[CC categories], which is less differentiated.)
|
41 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
4.2 |
Standardisation of the major diagnostic categories
|
42 |
Table 2:
Standardised major diagnostic categories |
| Code
| Short Label
| Label
|
| 00'
| Outpat.
| Outpatient Treatments
|
| 01'
| Nerves
| Nervous System
|
| 02'
| Eye
| Eye
|
| 03'
| ENT
| Ear, Nose, Mouth, and Throat
|
| 04'
| Respir.
| Respiratory System
|
| 05'
| Circul.
| Circulatory System
|
| 06'
| Digest.
| Digestive System
|
| 07'
| Hep+P
| Hepatobiliary System and Pancreas
|
| 08'
| MuscTs
| Musculoskeletal System and Connective Tissue
|
| 09'
| Skin
| Skin, Subcutaneous Tissue, and Breast
|
| 10'
| Endocr.
| Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases and Disorders
|
| 11'
| Kidney
| Kidney and Urinary Tract
|
| 12'
| Male
| Male Reproductive System
|
| 13'
| Female
| Female Reproductive System
|
| 14'
| Birth
| Pregnancy, Childbirth, and Puerperium
|
| 15'
| Neonat.
| Newborns and Other Neonates
|
| 16'
| Blood
| Blood and Blood Forming Organs and Immunological Disorders
|
| 17'
| Neopl.
| Myeloproliferative Diseases and Disorders, and Poorly Diffenerentiatad Neoplasms
|
| 18'
| Infect.
| Infectious and Parasitic Diseases
|
| 19'
| Mental
| Mental Diseases and Disorders
|
| 20'
| Drug
| Alcohol/Drug Use and Alcohol/Drug Induced Organic Mental Disorders
|
| 21'
| Trauma
| Injuries, Poisoning, and Toxic Effect of Drugs
|
| 22'
| Burns
| Burns
|
| 23'
| Div.Fac
| Factors Influencing Health Status and Other Contacts with Health Services
|
| 24'
| HIV
| Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infections
|
| 25'
| Polytr.
| Multiple Significant Trauma
|
| 85'
| Child
| Children
|
| 91'
| Trp+Trc
| Transplantations and Tracheostomies
|
| 92'
| Day1
| Death and Transfer Within One Day
|
| 99'
| Error
| Unclassifiable
|
|
43 |
|
Common base of MDCs |
[Table 2]
In order to have a common classification for the system comparisons,
the major diagnostic categories of the individual
patient classification systems were numbered and designated
in a standardised manner.
The major AP-DRG diagnostic
categories served for the reference classification.
The groups additionally defined by the Swiss APDRG Association
and the groups of exceptional and unclassifiable cases were renumbered.
For purposes of identification, an apostrophe (')
was placed behind each code number of the standardised system.
|
44 |
|
AR subcategory types |
In the AR-DRG system, three major diagnostic subcategory types
are defined:
"surgical", "medical" and "others".
The subcategory type "others" contains the ARDRGs
which are derived from non operating room procedures.
With regard to the common analysis,
these ARDRGs have been merged
with the "surgical" subcategory type.
|
45 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
4.3 |
Fractionation coefficient
|
46 |
|
Assessment of the fragmentation of a base DRG
|
By way of measurement for the assessment of the fragmentation
of the base groups within a DRG system, a so-called
"fractionation coefficient" was developed.
The higher the fractionation coefficient,
the more strongly a base DRG of the
"original" system to be assessed is divided up
among different base groups of the reference system.
To compute the fractionation coefficient for each
base DRGg of the original system,
the proportional distribution of the cases among
the base DRGsh
of the reference system is determined.
The greater these proportions, the less they contribute towards
the fragmentation. For this reason, the differences between
these proportions and 1 were calculated. These differences
were then weighted and summed up. The weights used were the
proportions themselves since the more cases were assigned to
an identical base DRGh,
the higher the relative influence
of these cases on the measure of fragmentation.
|
47 |
|
fg :
fractionation coefficient per base DRG
|
In mathematical terms, this looks as follows:
A base DRGg
from the original system G is represented in the h-indexed
base DRGs of the reference system H.
pgh
designates the proportion of the cases from
base DRGg which were classed
in base DRGsh of the reference system.
The fractionation coefficient is calculated as follows:
fg|H =
SUMMEh{ ( 1 – pgh ) pgh },
with: SUMMEh{ pgh } = 1,
or more simply:
fg|H = 1 – SUMMEh{ pgh2 }
|
48 |
Table 3:
Calculation examples for fractionation coefficients
|
| Distribution
| Nb. of groups
| Result
| Distribution
| Nb. of groups
| Result
|
| 100 %
| 1
| 0.000
| 67, 22, 11 %
| 3
| 0.490
|
| 99, 1 %
| 2
| 0.020
| 50, 50 %
| 2
| 0.500
|
| 98, 1, 1 %
| 3
| 0.039
| 50, 33, 17 %
| 3
| 0.612
|
| 90, 10 %
| 2
| 0.180
| 33, 33, 33 %
| 3
| 0.667
|
| 80, 20 %
| 2
| 0.320
| 10, . . ., 10 %
| 10
| 0.900
|
| 80, 13, 7 %
| 3
| 0.338
| 1, . . ., 1 %
| 100
| 0.990
|
| 67, 33 %
| 2
| 0.442
| 0.1, . . ., 0.1 %
| 1000
| 0.999
|
|
49 |
|
Examples
|
A few examples may serve as explanations:
[Table 3]
-
First example:
all the cases that have been assigned
to a certain base DRGg of the original system
are represented in one single
base DRGh in the reference system.
Such a 1:1 representation
results in a fractionation coefficient of:
f = 1 – 12 = 0.
-
Second example:
the cases that have been assigned to a
base DRGg are represented in two different
base DRGsh in the reference system in proportions of
90 % and 10 %.
This results in a fractionation coefficient of:
f = 1 – ( 0.92 + 0.12 )
= 0.18.
-
Third example:
the cases that have been assigned to a base DRGg
are represented in three different base DRGsh
in the reference system in proportions of
80 %, 13 % and 7 %.
This results in a fractionation coefficient of:
f = 1 – ( 0.82 + 0.132 + 0.072 )
= 0.34.
-
Fourth example:
the cases that have been assigned to a base DRGg
are represented in two different
base DRGsh in the reference at a ratio of 50:50.
This results in a fractionation coefficient of:
f = 1 – ( 0.52 + 0.52 )
= 0.5.
|
50 |
|
FG :
Average fractionation coefficient of a DRG system
|
To assess the correspondence between the representation
of all the cases from a original system G and in a reference
system H, a weighted average fractionation coefficient was computed.
The case numbers n per base DRGg served as weights:
FG|H =
SUMMEg{ ng fg|H }
/ SUMMEg{ ng }
|
51 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
4.4 |
Treemaps
|
52 |
33
Cf. Fischer [Krankenhaus-Betriebsvergleiche, 2005]: 113 ff;
Shneiderman [Treemaps, 1992].
34
Vgl.
Fischer [Krankenhaus-Betriebsvergleiche, 2005]: 113 ff;
Shneiderman [Treemaps, 1992].
|
Treemaps for the representation of entire DRG systems
|
By means of the treemaps21 generated in this study,
all the base DRGs of a DRG system are printed on one single page.
Each box represents one base DRG.
The size of the boxes reflects the proportion of cases it represents.
In this way, it points out the quantitative relevance
of the base DRGs depicted.
|
53 |
|
|
The first treemap variant shows
the fractionation coefficient
of the representation of each base DRG of the original system
in the reference system
by means of the values indicated and the colours of the boxes.
|
54 |
|
|
A second treemap variant was developed
which has higher degree of differentiation:
In the case of each base DRG,
it can be seen now to which alternative base DRGs of a reference
classification system it has been assigned.
|
55 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5 |
Results
|
56 |
|^·<×>·v| |
5.1 |
Number of base groups and number of case groups
|
57 |
Table 4:
Number of DRGs and base DRGs according to major diagnostic categories and subcategory types
|
|
58 |
Table 5:
Number of DRGs and base DRGs of each major diagnostic category according to the DRG system and subcategory types
|
59 |
|
|
|
Standardisation of the major diagnostic categories of DRGs
|
To compare the number of groups, the major diagnostic categories
of the individual DRG systems were numbered and labelled
in a standardised manner.
|
60 |
|
Key to the graphs |
[Tables 6
and 7]
The graphic representation of the count of DRGs and base DRGs
was effected in two different ways:
once according to DRG systems, and once according to the
DRG's major diagnostic categories.
For the rest, both graphs have the same structure:
the left half of the graph
– i. e. that half in which the yellow bars are located –
refers to surgical/procedural DRGs,
whilst the right half – that with the green bars –
refers to medical DRGs.
The outer figures indicate the number of DRGs
per major diagnostic subcategory,
the inner figures the number of base DRGs.
The four figures per line have been visualised by the bars.
|
61 |
|
Commentary |
A scrutiny of the graphs reveals the following striking features:
-
[Table 3]
The number of base groups differs.
It ranges from approximately 360 base groups in APR
and SQLape to approximately 560 base groups in IR.
-
Both the surgical and the medical subcategories
within one system contain very different numbers of
patient categories.
-
[Table 4]
The number of patient categories per major diagnostic category
varies greatly among DRG systems.
At least at first sight, hardly any regularities can be made out.
(One such observation would be, for instance,
that:
all DRG systems
have more medical than surgical DRGs
within the respiratory system [04'].
But even when we look at the number of base DRGs in this major
diagnostic category, the IR-DRG system proves to be an
exception of this rule . . .
At any rate,
concerning the musculoskeletal system [08']
there are more surgical DRGs
and also more base DRGs throughout this major diagnostic category.)
|
62 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5.2 |
Fractionation coefficients in pair comparisons of DRG systems
|
63 |
Table 6:
Map of the weighted average fractionation coefficients of pair comparisons of DRG systems
|
|
64 |
Table 7:
Weighted average fractionation coefficient of pair comparisons of DRG systems
|
|
65 |
|
Fractionation coefficient |
The "fractionation coefficient" was developed in order
to measure the extent of fragmentation that occurs
when hospital stays are classed according to two different DRGs.
In short: a fractionation coefficient of 0 indicates
a 1:1 representation.
The coefficient increases with the number of different base DRGs
of the reference system that are used to represent
the cases of a base DRG of the original system to be assessed.
However, it never exceeds 1.
|
66 |
|
|
Table 6
illustrates fractionation coefficients for pairs of
DRG systems. A value of
0.23
for "APR:AR" on the vertical
axis, which is labelled "System 1 → 2",
means that when the original system 1 (here: APR)
was represented in the reference system 2 (here: AR),
a fractionation coefficient of
0.23
was calculated for the cases contained in the database.
The assignment of DRGs corresponds better, the further to the
bottom left a pair of patient classification systems is placed.
|
67 |
|
|
An alternative depiction of these values is represented in
Table 7,
where the values of the fractionation coefficients are
actually printed out.
In addition, these values were coloured according to their height:
blue points to low (corresponding) values,
orange to high (diverging) values.
The size of the rectangles is proportionate to
the fractionation coefficient:
the smaller the symbol, the better the value.
|
68 |
|
|
|
|
|
APR and AP |
The evaluation of the fractionation coefficients reveals
that the APR and AP systems display the highest degree
of correspondence;
in Table 6,
the pair is placed bottom left.
The comparison resulted in average fractionation
coefficients of
0.1
or less. This means that there are many
cases in DRGs that have a similar concept in both cases.
|
69 |
|
APR and IR |
The comparison between APR and IR also yielded low
fractionation coefficients. The average fractionation
coefficients are below
0.12.
This means that here, too,
there are many cases with similar concepts in both the APR
and the IR system.
|
70 |
|
AR compared with APR and IR |
The next pairs we look at are APR and AR, and AR and IR.
Both entries are at a distinctive distance from the diagonal.
This means that fractionation weighs differently
depending on the direction of the representation.
In concrete terms, for instance,
the representation of APR in AR (with a value of
0.23)
is worse than the representation of AR in APR (with a value of
0.15).
It is striking that the representation of IR in AR,
with a value of
0.32,
is the most problematic of the
representations within the DRG pairs.
This figure makes it evident
that IR and AR are based on quite different concepts.
|
71 |
|
SQLape |
In the comparisons with the SQLape system,
which is based on a different concept,
the SQLape procedure category
that the system returned when only the main
diagnosis and the main procedure were grouped,
was used as the base group;
if no SQLape procedure category existed,
use was made of the
SQLape diagnosis category returned.
This code was called "SQp".
The different classification approach of the SQLape system
is reflected in relatively high fractionation coefficients.
They all exceed
0.42.
This shows that correspondence with conventional DRG systems is
relatively small.
|
72 |
|
|
Even greater divergences occur when the primary SQLape
categories ("SQ1") are compared with the base DRGs of the
various DRG systems. Here, the fractionation coefficients
even exceed
0.59. |
73 |
|
CCS |
The fractionation coefficients of the representation of
the medical base DRGs in the CCS diagnosis categories,
and of the surgical base DRGs in the CCS procedure categories
appear in the line labelled "CCS"
in Table 7.
The values are high throughout;
they range from
0.43
to
0.51,
i. e. all the DRG systems are relatively inhomogeneous
with regard to the CCS categories.
With 0.35,
the LDF system does not possess
a substantially better value.
The conspicuous exception is the representation of SQp in CCS,
where the fractionation coefficient is only
0.24.
|
74 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5.3 |
Fractionation coefficients according to major diagnosic subcategory types
|
75 |
Table 8:
Weighted average fractionation coefficient of pair comparisons of DRG systems according to major diagnostic subcategory types
|
76 |
|
|
|
|
The fractionation coefficients can also be computed
for subsystems of DRG systems. Below, the fractionation
coefficients for surgical and medical base DRGs will be
considered separately since it is known that the representation
quality for medical cases in DRG systems is markedly worse
than that for surgical cases.
|
77 |
|
Medical DRGs show a higher degree of correspondence than
surgical DRGs
|
When we look at
Table 8,
it is immediately apparent
that the DRG systems differ more strongly from each other
in the surgical field than they do in the medical field.
The high values of
the representation of the surgical base IR-DRGs both in AR
and in APR are particularly striking
(F.chirIR|AR =
0.43;
F.chirIR|APR =
0.37).
On the other hand,
a very high degree of correspondence occurs for the medical
cases grouped according to APR-DRG when the IR-DRG system
is used as the reference classification
(F.medAPR|IR =
0.06).
(F.chirAP|APR =
0.03;
F.medAP|APR =
0.04). |
78 |
|
SQLape |
The representation of the DRG systems in the SQLape code
for main procedure or main diagnosis (SQp) results in
poor fractionation coefficients for both major diagnostic
subcategory types. In the medical sphere they are slightly
better than in the surgical sphere, unless they are compared
with the base IR-DRGs. What is interesting is the fact that
SQp and SQ1 differ only slightly in relation to the surgical
base DRGs. In the medical sphere, however, the primary
SQLape categories "SQ1" differ much more strongly from the
medical base DRGs
than the SQLape main treatment categories "SQp".
|
79 |
|
|
It is striking that the fractionation coefficient of the
representation of the surgical SQp in the CCS procedures is
comparably low:
F.chirSQp|CCS is
0.21. |
80 |
|
CCS |
All in all, it appears that the medical base DRGs come somewhat
closer to the CCS diagnosis classification than the surgical
base DRGs come to the CCS procedure classification; however,
fragmentation is high in both areas. The representation
of APR in CCS is distinctly worse that the representation
of IR in CCS, with regard to both diagnoses and procedures
(F.chirAPR|CCS =
0.59
in comparison with
F.chirIR|CCS =
0.49
and
F.medAPR|CCS =
0.43
in comparison with
F.medIR|CCS =
0.34). |
81 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5.4 |
Fractionation coefficients according to major diagnosic subcategories
|
82 |
Table 9:
Weighted average fractionation coefficient of pair comparisons of DRG systems per system according to major diagnosis subcategories (Part 1)
|
83 |
|
|
Table 10:
Weighted average fractionation coefficient of pair comparisons of DRG systems per system according to major diagnosis subcategories (Part 2)
|
84 |
|
|
|
|
[Tables 9
and
10]
In the next step of the analysis,
the fractionation coefficients are computed
for each major diagnosis subcategory.
|
85 |
35
Fischer [Basis-DRG-Vergleiche, 2005].
36
Fischer [Basis-DRG-Vergleiche, 2005].
|
Here: DRG systems only |
In this instance, comparisons were limited to DRG systems
proper. Naturally, a comparison with SQLape, LDF and CCS
would also be of interest since it would reveal the areas in
which similarities might be found despite the overall great
divergences noted in the last chapter. In the basic study22, these comparisons were made.
For reasons of space and clarity, they will not be repeated here.
|
86 |
|
Large symbols
= great divergence
|
Large and yellowy-orange symbols indicate great discrepancies
between the systems concerned. Columns with a majority
of small rectangles show that the cases from the major
diagnosis subcategory type described above them
(C: "surgical/procedural" or M: "medical")
of the original system were grouped into
relatively similar base groups of the reference system
named below the column.
|
87 |
|
AP |
Areas with high degrees of correspondence exist, for example,
between AP and APR in the surgical subcategories
Eyes [02'C],
Circulatory system [05'C],
Digestive system [06'C],
Hepatobiliary system and pancreas [07'C],
Skin [09'C],
Glands, metabolism [10'C],
Male [12'C],
Female [13'C],
Birth [14'C] and
HIV [24'C].
For all these surgical subcategories,
the fractionation coefficient is below 0.05.
The Respiratory System [04'C] is
a striking exception to this rule.
|
88 |
|
IR |
It is striking in the comparison of the IR system
with the other DRG systems,
that there is distinctly more similarity
in the medical sphere than in the surgical sphere.
It must be assumed that this is linked to the fact that a new concept
was developed for the surgical sphere and that hospital
cases – unlike in the other DRG systems –
are assigned to a surgical IR-DRG independently of the main diagnosis.
|
89 |
Table 11:
Weighted average fractionation coefficient of pair comparisons of DRG systems according to surgical subcategories
|
90 |
|
|
Table 12:
Weighted average fractionation coefficient of pair comparisons of DRG systems according to medical subcategories
|
91 |
|
|
|
Problematischere und problemlosere Subkategorien |
Tables 11
and
12
help find those subcategories
which categorise hospital cases in a relatively similar
manner and those with greatly different grouping concepts.
|
92 |
|
"no problems" |
In the following, those subcategories for which all the
representations in other DRG systems resulted in fractionation
coefficients of less than
0.15
will be regarded as presenting "no problems" (at first sight).
|
93 |
|
"problematic" |
In the following, those subcategories for which at least
one of the representations in another DRG system among
all the DRG systems under scrutiny resulted in an average
fractionation coefficient of more than
0.5
will be considered to be (potentially) "problematic".
|
94 |
|
Surgical subcategories |
[Table 11]
Among the surgical subcategories, there is only one single
subcategory for which all the comparisons yielded low
fractionation coefficients, namely the category with the
transplantations and tracheostomies
[91'C]. |
95 |
37
At least one fractionation coefficient
is above 0.4 but below 0.5
in the subcategories
Circulary system [05'C];
Musculoskeletal system [08'C];
Male reproductive system [12'C].
38
Mindestens ein Fraktionierungskoeffizient liegt über 0.4
aber unter 0.5 in den Subkategorien:
Kreislauf [05'C];
Bewegungsapparat [08'C];
Mann [12'C].
|
|
All the other subcategories have fractionation coefficients
in excess of 0.4.
Only in three of these subcategories does none of
the fractionation coefficients exceed 0.5.23
|
96 |
|
Medical subcategories |
[Table 12]
Among the medical subcategories, too, there is only one
subcategory for which all the comparisons resulted in low
fractionation coefficients:
ENT [03'M].
|
97 |
|
|
The following medical subcategories display problematic
differences:
- 06'M: Digestive system
- 15'M: Newborns
- 19'M: Mental diseases
- 20'M: Drugs
- 24'M: HIV
- 25'M: Multiple significant trauma
- 99'M: Not groupable
|
98 |
|
Commentary |
There is an amazing number of subcategories with differing
grouping concepts. In all these cases, a closer look is
necessary to find the base DRGs that have been subjected to
particularly different treatment.
|
99 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5.5 |
Major diagnostic subcategories with more problems and with fewer problems
|
100 |
|
Problematischere und problemlosere Subkategorien |
Tables 11
and
12
help find those subcategories
which categorise hospital cases in a relatively similar
manner and those with greatly different grouping concepts.
|
101 |
|
"no problems" |
In the following, those subcategories for which all the
representations in other DRG systems resulted in fractionation
coefficients of less than
0.15
will be regarded as presenting "no problems" (at first sight).
|
102 |
|
"problematic" |
In the following, those subcategories for which at least
one of the representations in another DRG system among
all the DRG systems under scrutiny resulted in an average
fractionation coefficient of more than
0.5
will be considered to be (potentially) "problematic".
|
103 |
|
Surgical subcategories |
[Table 11]
Among the surgical subcategories, there is only one single
subcategory for which all the comparisons yielded low
fractionation coefficients, namely the category with the
transplantations and tracheostomies
[91'C]. |
104 |
39
At least one fractionation coefficient
is above 0.4 but below 0.5
in the subcategories
Circulary system [05'C];
Musculoskeletal system [08'C];
Male reproductive system [12'C].
40
Mindestens ein Fraktionierungskoeffizient liegt über 0.4
aber unter 0.5 in den Subkategorien:
Kreislauf [05'C];
Bewegungsapparat [08'C];
Mann [12'C].
|
|
All the other subcategories have fractionation coefficients
in excess of 0.4.
Only in three of these subcategories does none of
the fractionation coefficients exceed 0.5.24
|
105 |
|
Medical subcategories |
[Table 12]
Among the medical subcategories, too, there is only one
subcategory for which all the comparisons resulted in low
fractionation coefficients:
ENT [03'M].
|
106 |
|
|
The following medical subcategories display problematic
differences:
- 06'M: Digestive system
- 15'M: Newborns
- 19'M: Mental diseases
- 20'M: Drugs
- 24'M: HIV
- 25'M: Multiple significant trauma
- 99'M: Not groupable
|
107 |
|
Commentary |
There is an amazing number of subcategories with differing
grouping concepts. In all these cases, a closer look is
necessary to find the base DRGs that have been subjected to
particularly different treatment.
|
108 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5.6 |
Example of a treemap for the display of fractionation coefficients
|
109 |
Table 13:
Fractionation coefficients of base IR2005-DRGs divided according to base APR15-DRGs
|
110 |
|
|
Table 14:
Fractionation coefficients of base IR2005-DRGs divided according to base AR5-DRGs
|
111 |
|
|
|
|
Each of the following treemaps contains
all the base DRGs of a DRG system.
The colours represent the values of the fractionation coefficients
per base DRG of the original system
mapped to the reference system.
|
112 |
|
|
|
|
|
Hierarchical structuring |
The graphs are hierarchically divided up according to:
-
major diagnostic subcategory types (vertical main subdivision
according to "surgical/procedural" and "medical";
-
standardised major diagnostic subcategories
(such as "01'M Nerves";
horizontal fields with black frames);
-
base DRGs of the original classification with a white frame,
sorted by the values of the fractionation coefficient.
|
113 |
|
Codes |
The codes for the original classification have been entered
at the centre of each white-framed cell.
Possibly it is followed by the label of the base DRG
(or a short version of it) and the fractionation coefficient
if space is available.
The major diagnostic subcategories
have been entered in italics
on the left of each black-framed cell,
turned around 90° counter-clockwise.
|
114 |
|
Surface division |
The size of the rectangles reflects the proportion of cases
they represents.
With the help of the vertical subdivision,
which separates the cases according to
major diagnostic subcategory types,
it can be seen that all in all,
the database used contains fewer surgical/procedural cases (on the left)
than medical cases (on the right).
|
115 |
|
Colours |
The colours correspond to the values of the fractionation coefficients.
Low coefficients are shown in a bluish colour,
high coefficients in a reddish colour.
|
116 |
|
|
The bluer a white-framed cell,
the less fragmentated the representation of the displayed
base DRGs of the original system
in the base DRGs of the reference system.
|
117 |
|
Number of cases in the database |
The overall number of cases represented from the database is
indicated in the centre below the graph.
|
118 |
|
|
|
|
|
IR → APR |
[Table 13]
The first of the two following treemaps
displays the fractionation coefficients
of all base IR-DRGs
split into base APR-DRGs.
It is striking immediatly
that there are much more reddish and red boxes on the left
with the surgical base IR-DRGs
than on the right
with the medical base IR-DRGs.
A quite great number of medical base IR-DRGs with
fractionation coefficients of zero or nearly zero
can be seen on the right half.
(They are coloured in a bluish colour.)
This means that this graphic tells us, too,
that the medical base IR-DRGs are less fragmentated
into APR-DRGs
than the surgical base IR-DRGs:
the fractionation coefficient
(F.medIR|APR) of
the medical base IR-DRGs
only amounts to
0.03,
whilst the fractionation coefficient of
the surgical base IR-DRGs
(F.chirIR|APR) is at
0.37.
|
119 |
|
IR → AR |
[Table 14]
The next graphic shows the fractionation of base IR-DRGs
into base AR-DRGs.
In this graphic,
also the medical field is now coloured with a more intensive red,
but it is still less red than the surgical field.
Yet the latter appears to be even more fragmentated
than in the previous graph for IR to APR.
A look at the fractionation coefficients of both fields
shows likewise that, though they are higher,
they differ less:
F.medIR|AR =
0.24,
F.chirIR|AR =
0.43. |
120 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5.7 |
Example of a treemap for the comparison of two DRG systems
|
121 |
Table 15:
Base IR2005-DRGs divided according to base AR5-DRGs
|
122 |
|
|
|
|
[Table 15]
The next treemap below shows all the
base DRGs of the original system again (black-framed),
yet this time divided up into the
base DRGs of the reference system (white-framed).
|
123 |
|
|
|
|
|
Hierarchical structuring |
These treemaps are hierarchically divided up according to:
-
major diagnostic subcategory types (main subdivision
according to "surgical/procedural" and "medical");
-
standardised major diagnostic subcategories
(such as "01'M Nerves"; with a fine grey frame
at a right angle to the main subdivision);
-
base DRGs of the original classification (with a black frame);
-
base DRGs of the reference classification (with a white frame).
|
124 |
|
Codes |
The codes for the original classification have been entered in
italics at the bottom of each black-framed cell, while the
codes for the reference classification occupy the centre of
the white-framed cells. The major diagnostic subcategories
have also been entered in italics, but the letters have been
turned around 90° counter-clockwise.
|
125 |
|
Surface division |
The size of the rectangles reflects the proportion of cases
they represents.
The main subdivision distinguishes between
the surgical/procedural cases
and the medical cases.
|
126 |
|
Colours |
The colours were determined on the basis of the (sequential)
code numbers of the reference classification. White rectangles
indicate a combination of base DRGs and reference base DRGs
with fewer than three cases.
|
127 |
|
Correspondence of classifications
|
The fewer stripes and the fewer colours the field of a base
DRG contains, the better the base DRG in question corresponds
to the group structure of the reference classification.
|
128 |
|
Number of cases in the database |
The overall number of cases represented from the database is
indicated in the centre below the graph (or,
in the portrait format print-out, to the left of the graph).
|
129 |
|
|
|
|
|
Notes concerning interpretation |
The treemaps below can be interpreted as follows:
-
Large rectangles
refer to frequent codings or coding combinations.
-
The smaller the number of white-framed
base DRGs of the reference system within a base DRG of the
original system, the more similar the grouping concept used
for these base DRGs in both systems.
-
The more uniform the colour gradient,
the more base DRGs of the original system
are represented in base DRGs of the reference
system whose codes are assigned to similar thematic areas.
-
Conspicuous colours point to the fact
that the same hospital cases
are encoded in different thematic areas.
-
An in-depth analysis should not only compare the colours
but also the labels of the base DRGs of the original system
and the assigned base DRGs of the reference system.
-
If the reference classification has
a good clinical homogeneity,
then the graph may serve as a basis for an estimate of
the clinical homogeneity of the original classification.
|
130 |
|
|
|
|
|
IR → AR |
Basically, the colour pattern in
Table 15
looks rather calm.
This means that
the classifications have a similar overall structure:
the hospital cases are classified into similar
"coding zones" by both DRG systems.
|
131 |
|
|
A detailed observation reveals that there is a considerable
number of base IRDRGs that are represented in several base ARDRGs:
this is the case wherever a black-framed field is
divided up into several white-framed subsections.
|
132 |
|
|
The most striking are base IR-DRG fields that bear several
colours: in this case, the base ARDRGs into which this
base IR-DRG is divided also belong to subcategories that are
"further distant".
The most conspicuous example of this kind
is
base IRDRG 06140x (IP Other Digestive System Procedures)
almost in the centre of the graph.
The size of the field shows
that a relatively high number of hospital cases have
been assigned to this collective base IR-DRG. In the AR-DRG
system, the same cases can be found both in the subcategory
"Digestive system" [06'C] and under
"Female reproductive system" [13'C].
|
133 |
|
|
Another example that is plain to see is provided by the
strong fragmentation of the base IRDRGs of procedures on
the musculoskeletal system [subcategory 08'C].
The prevalent yellow colour shows that the base ARDRGs
according to which these cases were grouped
are frequently to be found in the same subcategory.
|
134 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5.8 |
Examples of individual DRG-related evaluations
|
135 |
Table 16:
Example:
APR 313 according to AR
(f=0.61,
n=21378):
Knee & lower leg procedures except foot |
136 |
| APR
| Cases
| %APR
| %AR
| Type
| MDC
| AR
| AR-DRG label
|
| 313
| 11204
| 52.4
| 74.7
| C
| 08
| I13
| Humerus, Tibia, Fibula and Ankle Procedures
|
| 313
| 6804
| 31.8
| 99.5
| C
| 08
| I18
| Other Knee Procedures
|
| 313
| 2549
| 11.9
| 98.9
| C
| 08
| I29
| Knee Reconstruction Or Revision
|
| 313
| 254
| 1.2
| 16.8
| C
| 08
| I12
| Infect/Inflam Bone & Joint
|
| 313
| 90
| 0.4
| 7.4
| C
| 08
| I21
| Local Excision & Removal of Internal Fixation Devices of Hip and Femur
|
| 313
| 88
| 0.4
| 1.5
| M
| ERR
| 961
| Unacceptable Principal Diagnosis
|
| 313
| 74
| 0.3
| 1.3
| M
| 08
| I75
| Injury to Shoulder, Arm, Elbow, Knee, Leg or Ankle
|
| 313
| 47
| 0.2
| 1.5
| C
| 08
| I28
| Other Connective Tissue Procedures
|
| 313
| 43
| 0.2
| 0.8
| C
| 08
| I20
| Other Foot Procedures
|
| 313
| 35
| 0.2
| 1.0
| M
| 08
| I69
| Bone Diseases & Spec Arthropathies
|
| 313
| 25
| 0.1
| 0.3
| C
| 08
| I08
| Other Hip and Femur Procedures
|
| 313
| 23
| 0.1
| 4.2
| C
| 21B
| X04
| Other Procedures for Injuries to Lower Limb
|
| 313
| 21
| 0.1
| 42.0
| C
| 08
| I11
| Limb Lengthening Procedures
|
| 313
| 18
| 0.1
| 0.4
| C
| 08
| I04
| Knee Replacement and Reattachment
|
| 313
| 17
| 0.1
| 0.5
| C
| 08
| I30
| Hand Procedures
|
| 313
| 16
| 0.1
| 1.0
| M
| 08
| I76
| Other Musculoskeletal Disorders
|
| 313
| 11
| 0.1
| 0.5
| M
| 01
| B60
| Established Paraplegia/Quadriplegia
|
|
|
Table 17:
Example:
APR 313 according to IR
(f=0.65,
n=21378):
Knee & lower leg procedures except foot |
137 |
| APR
| Cases
| %APR
| %IR
| Type
| MDC
| IR
| IR-DRG label
|
| 313
| 10484
| 49.0
| 97.6
| C
| 08
| 08170x
| IP Knee & Lower Leg Procedures Except Foot
|
| 313
| 6364
| 29.8
| 36.5
| C
| 08
| 08160x
| IP Other Musculoskeletel System & Connective Tissue Procedures
|
| 313
| 2482
| 11.6
| 19.2
| C
| 08
| 08140x
| IP Local Excision & Removal Of Internal Fixation Device
|
| 313
| 1100
| 5.1
| 15.2
| C
| 08
| 08150x
| IP Soft Tissue Procedures
|
| 313
| 831
| 3.9
| 10.6
| C
| 08
| 08130x
| IP Foot Procedures
|
| 313
| 46
| 0.2
| 1.9
| C
| 01
| 01120x
| IP Cranial & Peripheral Nerve Procedures
|
| 313
| 18
| 0.1
| 0.4
| C
| 04
| 04130x
| IP Moderately Complex Respiratory System Procedures
|
| 313
| 13
| 0.1
| 0.1
| C
| 05
| 05120x
| IP Other Circulatory System Procedures
|
| 313
| 12
| 0.1
| 0.3
| C
| 05
| 05106x
| IP Other Cardiothoracic Procedures
|
|
|
Table 18:
Example:
APR 313 according to AP
(f=0.59,
n=21378):
Knee & lower leg procedures except foot |
138 |
| APR
| Cases
| %APR
| %AP
| Type
| MDC
| AP
| AP-DRG label
|
| 313
| 11486
| 53.7
| 76.0
| C
| 08
| A-218
| Lower Extremity & Humerus Procedures Except Hip, Foot, Femur
|
| 313
| 7306
| 34.2
| 99.4
| C
| 08
| A-221
| Knee Procedures
|
| 313
| 1510
| 7.1
| 13.3
| C
| 08
| A-231
| Local Excision & Removal Of Int Fix Devices Except Hip & Femur
|
| 313
| 814
| 3.8
| 14.4
| C
| 08
| A-226
| Soft Tissue Procedures
|
| 313
| 110
| 0.5
| 8.3
| C
| 08
| A-230
| Local Excision & Removal Of Int Fix Devices Of Hip & Femur
|
| 313
| 63
| 0.3
| 2.4
| C
| 23
| A-461
| O.R. Procedures W Diagnoses Of Other Contact W Health Services
|
| 313
| 62
| 0.3
| 6.2
| C
| 25
| A-732
| Other O.R. Procedures For Multiple Significant Trauma
|
| 313
| 15
| 0.1
| 0.1
| M
| 27
| A-901
| Transfer Within One Day
|
|
|
|
Abbildungen in DRG-Systeme |
In the following, the fragmentation of the
base APR-DRG 313 (Knee & lower leg procedures except foot)
will be shown through its representation in the AR-DRG system,
in the IR-DRG system and in the AP-DRG system. The fractionation
coefficient is relatively high for all three representations,
namely
approximately f = 0.6. |
139 |
41
Foot procedures :
base APR-DRG 314 (Foot procedures);
base AR-DRG I20 (Other Foot Procedures).
42
Eingriffe am Fuss:
base APR-DRG 314 (Foot procedures);
base AR-DRG I20 (Other Foot Procedures).
43
There are separate DRGs in both systems for
replantations and prostheses:
base APR-DRG 301 (Major joint & limb reattach proc of lower extremity for trauma) und
base APR-DRG 302 (Major joint & limb reattach proc of lower extrem exc for trauma);
base AR-DRG I04 (Knee Replacement and Reattachment).
44
Für Replantationen und Prothesen gibt es in beiden Systemen
separate DRGs:
base APR-DRG 301 (Major joint & limb reattach proc of lower extremity for trauma) und
base APR-DRG 302 (Major joint & limb reattach proc of lower extrem exc for trauma);
base AR-DRG I04 (Knee Replacement and Reattachment).
|
APR 313 → AR |
[Table 16]
When the hospital cases from base APR-DRG 313
are represented in the AR-DRG system, it becomes evident
that these cases are mainly assigned to three base ARDRGs,
namely:
base AR-DRG I13 (Humerus, Tibia, Fibula and Ankle Procedures),
base AR-DRG I18 (Other Knee Procedures)
and
base AR-DRG I29 (Knee Reconstruction Or Revision).
As in APR, foot procedures are also represented in a separate DRG.25
Nevertheless, only half of the APR-313 cases
come into the nominally comparable base AR-DRG I13
(cf. column marked "%APR").
On the strength of the label of AR-DRG I13
it becomes clear that this also includes procedures on the humerus
(i. e. on the upper arm,
thus not only on the lower but also on the upper extremity).
This explains why only three quarters
of this base AR-DRG (I13) contains cases from base APR-DRG 313
(cf. column marked "%AR").
Evidently, the APR-DRGs in this context
are less differentiated at the level of base DRGs
than ARDRGs; part of this might be compensated for
by the four severity categories that
are systematically available in the APR-DRG system.
However, it turns out that in the AR-DRG system,
I13, too, has three severity categories
whereas I18 and I20 have no further subdivisions.26
|
140 |
45
Ein Teil dieser Unstimmigkeit rührt daher,
dass das Sprunggelenk das eine Mal zum Fuss gehört,
das andere Mal nicht.
46
Base IRDRG 08170x is solely preceded by "IP".
In the IR-DRG system, "IP" identifies all
stationary procedures (I = inpatient, P = procedure).
47
Bei base IRDRG 08170x ist einzig
"SP" vorangestellt.
Mit "SP" (englisch: "IP")
werden im IRDRG-System
alle stationären Eingriffe gekennzeichnet
(S = stationär, P = Prozedur).
|
APR 313 → IR |
[Table 17]
When the hospital cases from base APR-DRG 313
were represented in the IRDRG system, they were mainly
positioned in five base IRDRGs, namely:
base IRDRG 08170x (IP Knee & Lower Leg Procedures Except Foot),
base IRDRG 08160x (IP Other Musculoskeletel System & Connective Tissue Procedures),
base IRDRG 08140x (IP Local Excision & Removal Of Internal Fixation Device),
base IRDRG 08150x (IP Soft Tissue Procedures)
and, interestingly, 3.9 % of the cases also in
base IRDRG 08130x (IP Foot Procedures),
even though the label of APR-DRG 313 should really exclude
any procedures on the foot.
What is particularly confusing, however, is the fact
that the labels of base APR-DRG 313 and base IRDRG 08170x
are identical27, and
yet not even half of the APR-313 cases are assigned to base
IRDRG 08170x (cf. column marked "%APR").
At any rate, almost all the cases to be found in base IRDRG 08170x,
namely 97.6 %, are assigned to base APR-DRG 313
(cf. column marked "%IR").
|
141 |
Table 19:
Example:
AR I13 according to AP
(f=0.06,
n=14999):
Humerus, Tibia, Fibula and Ankle Procedures |
142 |
| AR
| Cases
| %AR
| %AP
| Type
| MDC
| AP
| AP-DRG label
|
| I13
| 14538
| 96.9
| 96.2
| C
| 08
| A-218
| Lower Extremity & Humerus Procedures Except Hip, Foot, Femur
|
| I13
| 220
| 1.5
| 22.0
| C
| 25
| A-732
| Other O.R. Procedures For Multiple Significant Trauma
|
| I13
| 101
| 0.7
| 7.0
| C
| 08
| A-217
| Wound Debridements & Skin Grafts
|
| I13
| 75
| 0.5
| 2.8
| C
| 23
| A-461
| O.R. Procedures W Diagnoses Of Other Contact W Health Services
|
| I13
| 27
| 0.2
| 1.1
| C
| 21
| A-442
| Other O.R. Procedures For Injuries
|
| I13
| 15
| 0.1
| 0.1
| M
| 27
| A-901
| Transfer Within One Day
|
|
|
Table 20:
Example:
AP A-218 according to AR
(f=0.07,
n=15115):
Lower Extremity & Humerus Procedures Except Hip, Foot, Femur |
143 |
| AP
| Cases
| %AP
| %AR
| Type
| MDC
| AR
| AR-DRG label
|
| A-218
| 14538
| 96.2
| 96.9
| C
| 08
| I13
| Humerus, Tibia, Fibula and Ankle Procedures
|
| A-218
| 155
| 1.0
| 10.3
| C
| 08
| I12
| Infect/Inflam Bone & Joint
|
| A-218
| 82
| 0.5
| 2.6
| C
| 08
| I28
| Other Connective Tissue Procedures
|
| A-218
| 59
| 0.4
| 1.1
| M
| 08
| I75
| Injury to Shoulder, Arm, Elbow, Knee, Leg or Ankle
|
| A-218
| 51
| 0.3
| 0.8
| M
| ERR
| 961
| Unacceptable Principal Diagnosis
|
| A-218
| 33
| 0.2
| 0.4
| C
| 08
| I08
| Other Hip and Femur Procedures
|
| A-218
| 31
| 0.2
| 1.7
| M
| 08
| I74
| Injury to Forearm, Wrist, Hand or Foot
|
| A-218
| 24
| 0.2
| 48.0
| C
| 08
| I11
| Limb Lengthening Procedures
|
| A-218
| 21
| 0.1
| 0.6
| M
| 08
| I69
| Bone Diseases & Spec Arthropathies
|
| A-218
| 20
| 0.1
| 1.2
| M
| 08
| I76
| Other Musculoskeletal Disorders
|
| A-218
| 15
| 0.1
| 0.3
| C
| 08
| I10
| Other Back and Neck Procedures
|
| A-218
| 11
| 0.1
| 0.5
| M
| 01
| B60
| Established Paraplegia/Quadriplegia
|
|
|
|
APR 313 → AP |
[Table 18]
When the hospital cases from base APR-DRG 313 were
represented in the AP-DRG system, they were mainly positioned
in five base AP-DRGs, namely
base AP-DRG A-218 (Lower Extremity & Humerus Procedures Except Hip, Foot, Femur),
base AP-DRG A-221 (Knee Procedures),
base AP-DRG A-231 (Local Excision & Removal Of Int Fix Devices Except Hip & Femur)
and
base AP-DRG A-226 (Soft Tissue Procedures).
This last base AP-DRG has a counterpart in the APR-DRG system,
namely
base APR-DRG 317 (Soft tissue procedures).
This raises the question as to whether
it is a positioning in APR-DRG 313 or an assignment
to base AP-DRG A-226 that fits the situation better.
|
144 |
|
|
|
|
|
Quervergleiche
AR I13 → AP |
[Table 19]
A complementary example to be shown is the representation
of the hospital cases from
base AR-DRG I13 (Humerus, Tibia, Fibula and Ankle Procedures)
in the AP-DRG system.
This is a relatively homogeneous representation:
96.9 % of the hospital cases in AR-DRG I13
will be found again in
base AP-DRG A-218 (Lower Extremity & Humerus Procedures Except Hip, Foot, Femur).
The representation also works well in the opposite
direction:
[Table 20]
96.2 % of the hospital cases in base AP-DRG A-218
are assigned to base AR-DRG I13.
This relatively good correspondence is also indicated
by the fractionation coefficients of
f = 0.06 and f = 0.07, respectively.
|
145 |
|
|
In this case, the different natures of AR and AP become
evident only at the next lower level.
Base AR-DRG I13 is divided up into three severity categories:
I13A applies to cases with severe or catastrophic comorbidities
or complications; all other cases are assigned to I13B
if patients are over 59 years of age,
whilst I13C is for patients under 60.
In contrast, there is APDRG 218 for
"Lower Extremity & Humerus Procedures Except Hip, Foot, Femur, Age > 17, with CC";
APDRG 219, the same, but without CC;
and APDRG 220 for patients below 18 years.
|
146 |
Table 21:
Example:
APR 313 according to SQp
(f=0.77,
n=21378):
Knee & lower leg procedures except foot |
147 |
| APR
| Cases
| %APR
| %SQp
| Type
| MDC
| SQp
| SQp label
|
| 313
| 8372
| 39.2
| 96.4
| C
| L
| CRU3
| Major operation on leg
|
| 313
| 4279
| 20.0
| 89.6
| C
| L
| GEN2
| Excision of knee structures
|
| 313
| 2590
| 12.1
| 33.9
| C
| L
| GEN4
| Open operation on knee
|
| 313
| 2350
| 11.0
| 41.4
| C
| L
| ART1
| Arthroscopy or traction
|
| 313
| 1133
| 5.3
| 65.3
| C
| L
| CRU2
| Minor operation on leg
|
| 313
| 697
| 3.3
| 14.6
| C
| L
| PED2
| Minor operation on foot
|
| 313
| 512
| 2.4
| 86.9
| C
| L
| GEN3
| Other arthroscopic operation on knee
|
| 313
| 425
| 2.0
| 21.4
| C
| L
| PED3
| Major operation on foot
|
| 313
| 225
| 1.1
| 2.5
| C
| L
| OSS2
| Removal of internal fixation device
|
| 313
| 109
| 0.5
| 3.7
| C
| L
| OSS4
| Other operation on unspecified bone
|
| 313
| 101
| 0.5
| 6.6
| M
| L
| L-tZ
| Other severe injury
|
| 313
| 93
| 0.4
| 13.9
| C
| L
| ART3
| Major operation on joint
|
| 313
| 64
| 0.3
| 3.4
| M
| L
| L-iO
| Musculoskeletal system inflammation
|
| 313
| 53
| 0.2
| 1.8
| C
| L
| MUS3
| Other operation on muscle
|
| 313
| 47
| 0.2
| 7.9
| M
| L
| L-dG
| Degenerative disease of knee
|
| 313
| 43
| 0.2
| 10.1
| C
| L
| OSS3
| Excision of unspecified bone
|
| 313
| 40
| 0.2
| 1.0
| M
| L
| L-tC
| Fracture of pelvis
|
| 313
| 37
| 0.2
| 2.2
| M
| L
| L-tJ
| Leg injury
|
| 313
| 37
| 0.2
| 1.2
| M
| L
| L-tL
| Other musculoskeletal injury
|
| 313
| 30
| 0.1
| 0.1
| M
| Z
| Z-zZ
| Other disorders
|
| 313
| 20
| 0.1
| 1.3
| C
| L
| ART2
| Minor operation on joint
|
| 313
| 19
| 0.1
| 1.2
| C
| L
| MUS2
| Excision or suture of muscle
|
| 313
| 17
| 0.1
| 0.1
| C
| T
| CUT1
| Minor operation on tegument
|
| 313
| 15
| 0.1
| 0.3
| C
| L
| BRA4
| Forearm minor operation
|
|
|
Table 22:
Example:
APR 313 according to SQ1
(f=0.74,
n=21378):
Knee & lower leg procedures except foot |
148 |
| APR
| Cases
| %APR
| %SQ1
| Type
| MDC
| SQ1
| SQ1 label
|
| 313
| 9003
| 42.1
| 94.7
| C
| L
| CRU3
| Major operation on leg
|
| 313
| 4647
| 21.7
| 88.1
| C
| L
| GEN2
| Excision of knee structures
|
| 313
| 3803
| 17.8
| 42.6
| C
| L
| GEN4
| Open operation on knee
|
| 313
| 713
| 3.3
| 91.2
| C
| L
| GEN3
| Other arthroscopic operation on knee
|
| 313
| 621
| 2.9
| 59.3
| C
| L
| CRU2
| Minor operation on leg
|
| 313
| 608
| 2.8
| 23.0
| C
| L
| PED3
| Major operation on foot
|
| 313
| 591
| 2.8
| 14.5
| C
| L
| PED2
| Minor operation on foot
|
| 313
| 177
| 0.8
| 3.6
| M
| Z
| Z-zM
| Without valid information
|
| 313
| 161
| 0.8
| 4.3
| C
| L
| MUS3
| Other operation on muscle
|
| 313
| 148
| 0.7
| 1.8
| C
| L
| OSS2
| Removal of internal fixation device
|
| 313
| 146
| 0.7
| 15.4
| C
| L
| ART3
| Major operation on joint
|
| 313
| 113
| 0.5
| 6.8
| C
| L
| ART2
| Minor operation on joint
|
| 313
| 62
| 0.3
| 11.4
| C
| L
| OSS3
| Excision of unspecified bone
|
| 313
| 48
| 0.2
| 1.3
| M
| L
| L-iO
| Musculoskeletal system inflammation
|
| 313
| 39
| 0.2
| 0.5
| C
| L
| COX4
| Other major operation on hip
|
| 313
| 38
| 0.2
| 1.3
| C
| L
| OSS4
| Other operation on unspecified bone
|
| 313
| 33
| 0.2
| 0.4
| M
| N
| N-fC
| Epilepsy
|
| 313
| 32
| 0.1
| 12.5
| C
| L
| COX3
| Minor operation on hip
|
| 313
| 24
| 0.1
| 1.3
| C
| N
| NER3
| Operation on nerves
|
| 313
| 23
| 0.1
| 0.2
| M
| U
| U-iU
| Urinary infection
|
| 313
| 22
| 0.1
| 2.1
| M
| L
| L-tZ
| Other severe injury
|
| 313
| 21
| 0.1
| 0.6
| C
| L
| SCA3
| Other major operation of shoulder
|
| 313
| 15
| 0.1
| 0.2
| C
| C
| COR2
| Heart operation without circulatory assistance
|
| 313
| 15
| 0.1
| 0.1
| M
| S
| S-mS
| Lymphoma, other leukemia or hematopoetic malignat neoplasm without complication
|
| 313
| 13
| 0.1
| 0.1
| C
| D
| ABD3
| Unilateral repair other hernia
|
| 313
| 12
| 0.1
| 0.4
| M
| P
| P+xS
| Chronic substance abuse
|
| 313
| 11
| 0.1
| 0.5
| M
| C
| C-zC
| Other cardiac disease
|
| 313
| 11
| 0.1
| 0.3
| M
| L
| L-tC
| Fracture of pelvis
|
| 313
| 10
| 0.0
| 0.2
| C
| C
| VAS2
| Operation on varicose limb veins
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Abbildungen nach SQLape
APR 313 → SQp |
[Table 21]
The representation of the hospital cases
of base APR-DRG 313
within the reference classification of
SQLape main treatment categories (SQp)
reveals that main treatments comprise
mainly procedures on the leg ("CRU"),
especially on the knee ("GEN")
and also
– inspite of the exclusion done by the APR-DRG label –
on the foot ("PED2" and "PED3").
|
149 |
|
APR 313 → SQ1 |
[Table 22]
The representation of the hospital cases
of base APR-DRG 313
within the reference classification of
primary SQLape categories (SQ1) is even more interesting.
They mirror the main treatments or diagnoses
determined by the SQLape system
based on the evaluation of all diagnoses and procedure codes.
The fragmentation is slightly smaller.
The first three SQ1 categories cover approximately 80 %
of the hospital cases.
The first seven SQ1 categories concern
the legs ("CRU"),
the knees ("GEN")
and the foots ("PED").
It would be worthwhile to take a look at the case data
in order to judge
if SQLape or APR did the groupings
of the "PED" cases
and of the hospital cases left over
in a more adequate manner.
|
150 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
6 |
Discussion and prospects
|
151 |
|
|
It has been revealed that the fractionation coefficient is
basically an interesting measure to describe
the relative difference in the nature of patient classification systems.
|
152 |
|
|
In the following, a number of discussion points are listed,
which at the same time serve as suggestions for further work.
|
153 |
|
|
|
|
48
Base DRGs can be subsumed in "DRG classes",
i. e. a kind of "product groups" or "product lines",
according to thematic resemblance.
Cf. among others
Krüger/Lenz [2004];
http:// www.adimehp.com / G-GHM.htm;
Buronfosse et al. [OAP manuel 3.0, 2003];
Buronfosse et al. [OAP court séjour, 2002];
Ruiz [GA+GF, 1999],
as well as the "product lines" in the PMC system:
PRI [PMC-Rel.5, 1993].
49
base DRGs
können nach inhaltlicher Zusammengehörigkeit
in "DRG classes",
in einer Art "Produktegruppen"
oder "Produktelinien" zusammengefasst werden.
Vgl. dazu u. a.:
Krüger/Lenz [2004];
http:// www.adimehp.com / G-GHM.htm;
Buronfosse et al. [OAP manuel 3.0, 2003];
Buronfosse et al. [OAP court séjour, 2002];
Ruiz [GA+GF, 1999]
sowie die "Produktelinien" im PMC-System:
PRI [PMC-Rel.5, 1993].
|
|
Standardisation of the major diagnostic categories:
-
Following the example of the IR-DRG system,
major diagnostic categories with few groups and hospital cases
could be subsumed.
This would concern HIV, for instance,
which would be assigned to infections,
or polytraumata,
which would be divided up among various major diagnostic
categories.
-
The DRGs of the former major diagnostic category
of transplantations and tracheostomies was dispersed
within the IR-DRG system.
In analogy, the base DRGs in other DRG systems
could be removed from this major diagnostic category
and assigned to the main categories of the organ systems concerned.
-
Besides major diagnostic categories, "DRG classes"
could be introduced as an additional hierarchical level,
which would serve to unite similar base DRGs in a tighter
structure.28
|
154 |
|
|
Base DRGs:
-
The definition of base DRGs could be made more precise.
In this manner, additional individual DRGs could be subsumed
even though the manufacturer defined them as separate DRGs.
|
155 |
50
Um z. B. zu untersuchen,
wo es Verschiebungen in andere Subkategorien gegeben hat,
könnten bei der Berechnung der Fraktionierungskoeffizienten
die Gewichtungen von Abbildungen innerhalb
der Subkategorie der zu beurteilenden base DRG
auf Null gesetzt werden.
|
|
Fractionation coefficient:
-
In the weighting process, a distinction could be introduced
between groups of the reference system that are positioned
within the same DRG subcategory (or within the same
DRG class; cf. above) and others.
-
In the aggregation of the fractionation coefficients
at the level of subcategory types and at system level,
the error groups could be excluded or given special
treatment. (In particular, this is necessary where the
nature of the system results in many false classifications,
as for instance with LDF, where transcoding obviously
still has many deficiencies.)
-
The influence of the number of groups
upon the fractionation coefficient
still needs to be examined.
|
156 |
|
|
Treemaps:
-
The size of the boxes could be calculated
by means of the weighted numbers of cases.
Therewith, they would be proportional to the revenues.
-
At present, the colouring of the base DRGs of the reference
system is based directly on their code numbers.
This will yield acceptable results particularly if the system
under scrutiny is structured according to a hierarchy that
is similar to that of the reference system. It would be
better, however, to colour base DRGs on the basis of a
common logical order that would still have to be defined.
|
157 |
|
|
Pair analysis of patient classification systems:
-
So far, a detailed view of individual base DRGs of a
original system and their breakdown according to basic
case groups of the reference classification has only been
provided by means of examples. This should be systematised.
-
Some information could be added
about the proportions of the cost weights.
-
A way of representing the breakdown of a base DRG
into several selected reference classifications should be developed.
-
Comparisons between DRGs and SQLape categories still
require further development.
|
158 |
|
|
Thematic comparisons:
-
DRG systems could be compared with each other in thematic
terms, as some examples adduced in this text have shown.
|
159 |
51
Cf. Rieben et al. [Pfadkostenrechnung, 2003]: 29 ff.
52
Vgl. Rieben et al. [Pfadkostenrechnung, 2003]: 29 ff.
|
|
Further fields of application:
-
The fractionation coefficient can be used to analyse
the correspondence between a DRG system and an alternative
patient classification system (such as the »mipp› system29 used by individual hospitals in the Swiss Canton of Aargau).
-
The fractionation coefficient and treemaps in particular
could be used to detect
coding differences within individual DRGs.
-
The fractionation coefficient and treemaps
could be used to visualise differences
of versions of a single DRG system
from year to year.
|
160 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
7 |
Appendix
|
161 |
|^·<×>·v| |
7.1 |
Table of abbreviations
|
162 |
Table 23:
Abbreviations and Links |
163 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
7.2 |
References
|
164 |
|
-
3M
- AP-DRG-CH
1998
| 3M Health Information Systems. AP-DRGs All Patient Diagnosis Related Groups Version 12.0. Adapted for Switzerland 1.0, Definitions Manual. Wallingford Borken 1998: 1408 pp. | 165 |
|
-
APDRG-CH
- CW 4.1
2003
| APDRG Schweiz. Kostengewichte Version 4.1. Prilly (ISE) 2003.
Internet (obsolete): http:// www.isesuisse.ch / de / apdrg / o_rapport_cw_v41_d.pdf. | 166 |
|
-
BFS-CH
- Medizinische Statistik
1997
| Bundesamt für Statistik. Statistik der stationären Betriebe des Gesundheitswesens. Medizinische Statistik. Detailkonzept 20.5.97, Bern 1997. | 167 |
|
-
BMGF-A
- LKF05-Modell
2004
| Bundesministerium für Gesundheit und Frauen [Hrsg.]. Leistungsorientierte Krankenanstaltenfinanzierung – LKF. Modell 2005. Wien (BMGF) 2004: 42 pp. Internet:
http:// bmgf.cms.apa.at / cms / site / attachments / 4 / 6 / 6 / CH0036 / CMS1039004330660 / modell_2005.pdf. | 168 |
|
-
Buronfosse et al.
- OAP court séjour
2002
| Buronfosse A, Duportail P, Delhommeau A, Martin S, Lepage E. Utilisation de l'outil d'analyse PMSI (OAP) court séjour. In: Info en santé 2002/1: 3–5. Internet:
http:// fhf.ecritel.net / fhf / docs / lettreinfo / infosante1.pdf. | 169 |
|
-
Buronfosse et al.
- OAP manuel 3.0
2003
| Buronfosse A, Discazeaux, Echard, Lellouch, Vollaire. Classification OAP: version 3.0 (Analyse des données PMSI 2002). Manuel d'utilisation. (Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris) 2003: 6 pp. Internet:
http:// gimep.free.fr / oap_v30.zip. | 170 |
|
-
Fetter et al.
- DRGs
1991
| Fetter RB, Brand A, Dianne G [Hrsg.]. DRGs, Their Design and Development. Ann Arbor (Health Administration Press) 1991: 341 pp. | 171 |
|
-
Fischer
- PCS
1997
| Fischer W. Patientenklassifikationssysteme zur Bildung von Behandlungsfallgruppen im stationären Bereich. Prinzipien und Beispiele. Bern und Wolfertswil (ZIM) 1997: 514 pp. Auszüge:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / studien / PCS-Buch-9701-Info.htm. | 172 |
|
-
Fischer
- IAP-DRG
1999
| Fischer W. Ein weiteres DRG-System: Die IAP-DRG. In: SGMI-Bulletin 1999/42: 20–24. Internet (mit Ergänzungen zu IR-DRG):
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / artikel / IAP-DRG-9909.htm. | 173 |
|
-
Fischer
- DRG-Systeme
2000
| Fischer W. Diagnosis Related Groups (DRGs) und verwandte Patientenklassifikationssysteme. Kurzbeschreibungen und Beurteilung. Wolfertswil (ZIM) 2000: 181 pp. Internet:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / studien / DRG-Systeme-0003-Info.htm. | 174 |
|
-
Fischer
- DRG+Pflege
2002
| Fischer W. Diagnosis Related Groups (DRGs) und Pflege. Grundlagen, Codierungssysteme, Integrationsmöglichkeiten. Bern (Huber) 2002: 472 pp. Auszüge:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / studien / DRG-Pflege-0112-Info.htm. | 175 |
|
-
Fischer
- Basis-DRG-Vergleiche
2005
| Fischer W. Vergleich von Basis-DRGs verschiedener DRG-Systeme. Auswertungen zur klinischen Homogenität der Systeme: APR-DRG 15, AR-DRG 5, IR-DRG 2005, SQLape 2005. Grundlagenpapier für das SwissDRG-Teilprojekt 2 (unveröffentlicht), Wolfertswil 2005: 114 pp. Publikation dazu:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / studien / PCS-Vergleiche-0511-Info.htm. | 176 |
|
-
Fischer
- Paarweise PCS-Vergleiche
2005
| Fischer W. Paarweise Vergleiche von Patientenklassifikationssystemen. Basis-DRGs, Fraktionierungskoeffizient und Belegungsdiagramme zur Beurteilung der relativen klinischen Homogenität von DRG-Systemen. Wolfertswil (ZIM) 2005: 51 pp. Internet:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / studien / PCS-Vergleiche-0511-Info.htm. | 177 |
|
-
Fischer
- Krankenhaus-Betriebsvergleiche
2005
| Fischer W. Neue Methoden für Krankenhaus-Betriebsvergleiche. Ein Werkstattbuch zur Visualisierung DRG-basierter Daten. Wolfertswil (ZIM) 2005: 160 pp. Auszüge:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / studien / KBV-0506-Info.htm. | 178 |
|
-
Fischer
- Relative clinical homogeneity
2006
| Fischer W. Base-DRGs, Fractionation Coefficient, and Treemaps for the Assessment of the Relative Clinical Homogeneity of DRG Systems. In: Revue économique et sociale, Lausanne 2006(64)special issue: 111–144. Internet:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / paper-en-pdf / Relative-Clinical-PCS-Homogeneity-0509.pdf. (The study in hand) | 179 |
|
-
Freeman JL et al.
- 1991
| Freeman JL, Fetter RB, Park H, Schneider KC, et al. Refinement. In: Fetter et al. [DRGs, 1991] 1991: 57–78. | 180 |
|
-
Krüger/Lenz
- 2004
| Krüger R, Lenz MJ. G-APDRG: Ein synthetisches Beschreibungsmodell der Krankenhausleistungen, entwickelt auf der Grundlage der G-GHM. In: 5. Deutsche Casemix-Konferenz, Konferenzdokumentation 2004: 257–264. | 181 |
|
-
Mullin et al.
- IR-DRG
2002
| Mullin R, Vertrees J, Freedman R, Castion R, Tinker A. Case-Mix Analysis Across Patient Populations and Boundaries. A Refined Classification System Designed Specifically for International Use. 2002: 6 pp.
Internet (obsolete): http:// www.3m.com / us / healthcare / his / pdf / reports / ir_drg_whitepaper_09_02.pdf. | 182 |
|
-
PRI
- PMC-Rel.5
1993
| PRI (The Pittsburgh Research Institute). Patient Management Categories. A Comprehensive Overview. Pittsburgh (The Pittsburgh Research Institute) 1993: approx. 65 pp. | 183 |
|
-
Rieben et al.
- Pfadkostenrechnung
2003
| Rieben E, Müller HP, Holler T, Ruflin G. Pfadkostenrechnung als Kostenträgerrechnung. Kalkulation und Anwendung von Patientenpfaden. Landsberg (ecomed) 2003: 279 pp. | 184 |
|
-
Roeder et al.
- G-DRGs 2005 Teil 2
2004
| Roeder N, Fiori W, Bunzemeier H, Fürstenberg T, Hensen P, Loskamp N, Franz D, Glocker S, Wenke A, Reinecke H, Irps S, Rochell B, Borchelt M. G-DRG-System 2005: Was hat sich geändert? (II). Spezifische Änderungen in medizinischen Leistungsbereichen. In: Das Krankenhaus 2004/12: 1022–1039. Internet:
http:// www.drg-research.de / de / downloads / literatur / kh1204_drg2005_teil_2.zip. | 185 |
|
-
Ruiz
- GA+GF
1999
| Ruiz J. PMSI et Groupes de produits. Exemple: Groupes fonctionnels, Groupes d'activités. 1999: 4 pp. Download _if_en(from,ab):
http:// www.adimehp.com / GAGF.htm. | 186 |
|
-
Schwab/Meister
- CMI
2004
| Schwab P, Meister A. Der Case Mix Index – ein Mass für den durchschnittlichen Schweregrad der Krankenhausfälle. Neuchâtel (Bundesamt für Statistik) 2004: 33 pp. | 187 |
|
-
Shneiderman
- Treemaps
1992
| Shneiderman B. Tree visualization with tree-maps. 2-d space-filling approach. In: ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 1992(11)1: 92–99. | 188 |
|
-
Wahrig
- Wörterbuch
1975
| Wahrig G. Deutsches Wörterbuch. Gütersloh Berlin München Wien (Bertelsmann) 1975: 1483 pp. | 189 |
|
-
Zahnd
- CCS
2003
| Zahnd D. Medizinischen Statistik der Krankenhäuser: Clinical Classification System (CSS). Ein Hilfsmittel für die Auswertung der Medizinischen Statistik. In: CodeInfo (2/03) 2003/14: 5–11. Internet:
http:// www.bfs.admin.ch / bfs / portal / de / index / themen / gesundheit / uebersicht / blank / publikationen.Document.48977.html. | 190 |
|
-
Zahnd
- CCS
2004
| Zahnd D. Die Analyse von Diagnose- und Behandlungsdaten mit dem CCS System. Eine «zweite Sicht» auf DRGs. In: 5. Deutsche Casemix-Konferenz, Konferenzdokumentation 2004: 38–41. | 191 |
![[print]](../PIC/e-div/print.gif)
![[pdf icon]](../PIC/e-div/pdf.gif) pdf file
(350 KB)
pdf file
(350 KB) Deutscher Text
Deutscher Text