|^·<×>·v| |
1 |
Abstract
|
1 |
|
Introduction |
Patient Classification Systems are constructed by collapsing similar diagnoses and/or treatments into not too many discrete groups, typically about 500 to 1000. These patient categories are usable if their labels are comprehensible.
In this study, the complexity of the DRG labels of several DRG systems is explored over time. |
2 |
|
Data |
DRG systems used in the USA (Medicare DRG 1994 until 2008), in Australia (AN-DRG 3.1, AR-DRG 4.1, AR-DRG 5.2), and in Germany (G-DRG 2003 until 2008) were inspected. As data, only the DRG labels had to be looked at. |
3 |
|
Methods |
For each DRG label, the following conjunctions were counted: "and", "or", "with", "without", "except"; commas, slashes, pairs of brackets and the word "age". Sequenced conjunctions are counted as 1. |
4 |
|
Results |
Whereas the number of conjunctions used in labels of Medicare DRGs stays relatively unchanged over time (the quota of labels with four or more conjunctions increases from 9 % to 11 %), there is some change within the labels from AN-DRG 3.1 through AR-DRG 4.1 to AR-DRG 5.2 (11 / 15 / 13 %). In contrast, there is a great increase in the use of conjunctions in the G-DRG labels (17 % to 49 %). |
5 |
|
Discussion |
The use of conjunctions does not only impair the comprehensibility of DRG labels but sometimes makes expressions ambiguous or practically unintellegible.
To get better DRG labels, it could be of help to use logical brackets, to split up complex DRGs for clinical homogeneity, or to construct patient classification systems for use in "cushioned" remuneration systems. |
6 |
|
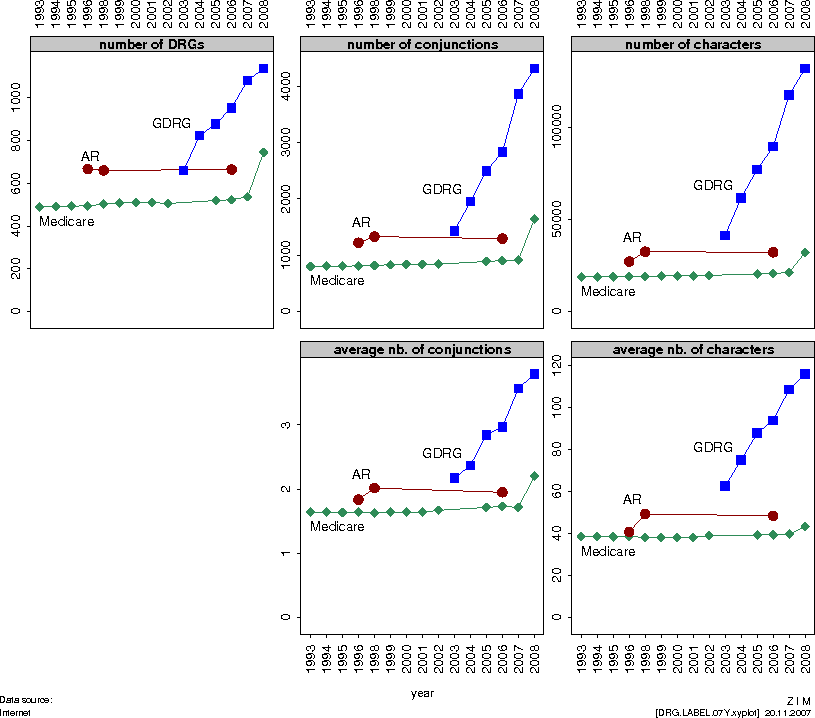
Conclusion |
A DRG system should not only be useful for statisticians, but it should also serve as a basis for discussions between clinicians and managers. Thus it is necessary to make sure that DRG labels are compehensible. This is especially important when DRG systems are strongly optimised with regard to statistical performance (as was done with the G-DRG system). |
7 |
|
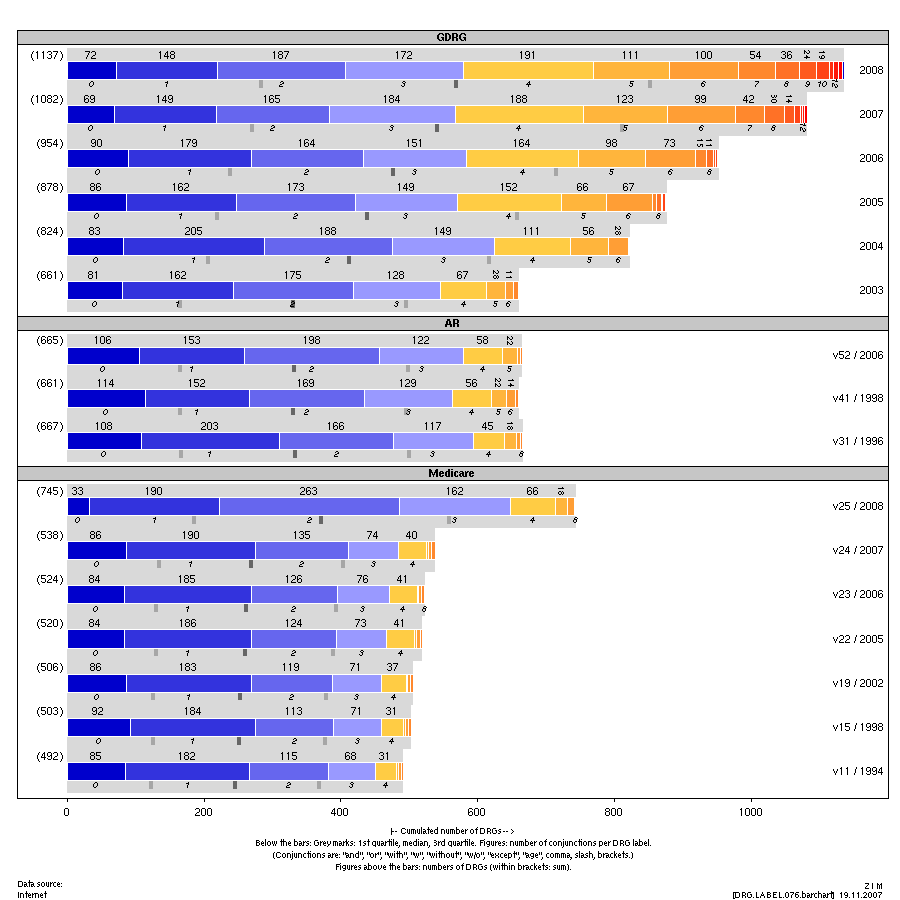
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
2 |
Introduction
|
8 |
1
DRG = Diagnosis Related Groups.
Cf. Fetter et al. [DRGs, 1991];
Fischer [PCS, 1997].
|
When is a language easy to use? |
When you learn a new language,
it will be easier if you already know some similar words
from other languages you have learnt before.
And you are more at ease if the new language does not use
excessively complex structures.
–
A DRG system1
contains a list of labels of patient categories (DRGs)
which are offered to be used during discussions between
managers and clinicians.
This offer will be accepted as a matter of course
the more the words used within the DRG labels are comprehensible
and the more the structure of the DRG labels is not excessively complex. |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
DRG systems as interdisciplinary tool |
Patient Classification Systems are constructed
by collapsing similar diagnoses and/or treatments
within not too many discrete groups, typically about 500 to 1000.
The aim was to get a handy and
comprehensible list of names of clinical treatments
that could be used as a basis for managerial discussions and decisions
of clinicians and managers.
Furthermore, the patient categories
should serve as "production units"
within a remuneration system. |
10 |
|
DRG lists must be handy |
Since the beginning of DRG history,
it was always a challenge to get a list
with not too many entries.
Patient categories should be clinically meaningful.
And from the economic viewpoint they should be expected
to generate similar costs. |
11 |
|
Base DRGs |
The general approach was to define a list of "Base DRGs"
("Adjacent DRGs") and additional criteria such as age
and lists of complications and comorbidities ("CC lists")
which could serve to split Base DRGs into subgroups
which are statistically as consistent as possible. |
12 |
2
Examples of statistically based splitting of Base DRGs
are Medicare DRGs, APDRGs, ARDRGs.
There are: only binary splits (e. g. Medicare DRGs);
splits with three levels
(e. g. APDRGs "without CC", "with CC"
and "with major CC"); or even more sophisticated systems
(e. g. ARDRGs, GDRGs).
|
DRG systems:
– with selected splits |
Two approaches to construct subgroups (named "DRGs"
were developed:
the first was to split only selected Base DRGs
into statistically different subgroups.
This resulted in DRG lists of typically 500 to 700 DRGs.2 |
13 |
3
Examples of DRG systems with general splits are
RDRGs, APR-DRGs, IR-DRGs (version 1).
|
– with general splits |
The second approach was to split all Base DRGs
according to the same criteria.
Normally, the selected criteria created several split levels
according to the severity of the diagnoses.
This resulted in systems with typically more than 1000 DRGs.3 |
14 |
|
Variance reduction |
The statistical goodness of the resulting patient categories
("DRGs")
is usually expressed by measuring the explained proportion of variance
of the dependent variable (usually length of stay or treatment costs)
in comparison to the variance which results when the patients are
not categorised.
It is called "variance reduction" (R2).
Its value ranges from zero (the groups do not explain any variance)
to 1 (the groups are able to explain the full variance). |
15 |
|
|
The first DRG systems achieved R2 values ranging
from 10 % to 30 %,
sometimes 40 % or later even nearly 50 %.
From a statistical viewpoint, these were not overwhelming results.
But by using more exact methods of cost calculation
and exploiting all statistical possibilities,
one got higher R2 values. |
16 |
Table 1:
G-DRG: Variance reduction of costs |
| Year
| R2 in %
all cases
| R2 in %
trimmed
| Number of DRGs
|
| 2007
| 70.7
| 80.5
| 1'082
|
| 2006
| 68.1
| 78.9
| 954
|
| 2005
| 63.9
| 78.0
| 878
|
| 2004
| 55.3
| 70.0
| 824
|
| 2003
| 46.6
| 62.3
| 664
|
|
17 |
|
G-DRG with astonishingly high R2 values |
[Table 1]
An exceptionally estonishing example is the G-DRG system:
the version of 2003 was a mapping of the Australian AR-DRG system 4.1.
At that time, with 664 DRGs, a R2 of 46.6 % was achieved
(trimmed: 62.3 %).
The actual version for 2007 comprises 1082 DRGs
and explains 70.7 % (trimmed: 80.5 %) of the variance.
This is a value which is high as one only dreamed at before. |
18 |
|
|
In this paper,
I want to look into
one side-effect of this statistically excellent result:
what effects did this refinement work
have on the comprehensibilty of the DRG labels? |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
3 |
Data
|
20 |
4
Medicare DRG: http:// www.apc-solutions.net / feds.htm and
http:// cms.hhs.gov / AcuteInpatientPPS / FFD /;
AN-DRG and AR-DRG: http:// www.health.gov.au / internet / main / publishing.nsf / Content / health-casemix-ardrg1.htm
and previous web pages;
G-DRG: http:// www.g-drg.de /.
|
|
The following DRG systems that are used in
the USA (Medicare DRG 1993/94 until 2007),
in Australia (ANDRG-3.1, ARDRG-4.1, ARDRG-5.2),
and in Germany (GDRG-2003 until 2007)
were inspected.
As data, only the DRG labels had to be looked at.
These were available on the internet.4 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
4 |
Methods
|
22 |
|
Counting conjunctions |
One aspect of comprehensibility is the logical structure of a statement.
In the case of DRG labels, a question can be:
how many different expressions for diagnoses and
other information are put together?
The hypothesis is that each block of words between
conjunctions (i. e. words which join terms)
can be understood as a logical (and comprehensible) unit.
The formal complexity of a DRG label can then be counted
by the number of the conjunctions used. |
23 |
5
"OR" at the end of a label is not counted because
this signifies "operation room (procedure)".
6
The correspondig German words were:
"und",
"oder",
"mit"/"bei",
"ohne",
"ausser",
"Alter".
|
|
The conjunctions which were counted for each DRG label, were:
"and", "or"5, "with", "without", "except",
commas, slashes, pairs of brackets
and the word "age".6
If conjunctions were sequenced, they were counted as one only conjunction. |
24 |
7
The list of conjunctions was given as a "regular expression"
to a program written in perl (http:// www.perl.org /).
|
|
A little computer program was written to count these words.7 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5 |
Results
|
26 |
|^·<×>·v| |
5.1 |
Overview
|
27 |
Table 2:
DRG labels: number of groups, conjunctions, characters
|
28 |
|
|
|
Growth of number of groups, conjunctions and characters |
[Table 2]
The graphic above
shows on the first line of graphic panels
the growth of the total numbers of DRGs,
of conjunctions and of characters used for the DRG labels.
On the second line of panels
the growth of the average numbers
of conjunctions and of characters is shown. |
29 |
|
|
It is remarkable that the change of these numbers for the Australian DRGs
(labelled as «AR») is negligible compared
to the growth of the same numbers for the German DRGs. |
30 |
|
|
Medicare DRGs shows a very little growth until 2007.
A visible change went with the shift to the refined MSDRG-System in 2008. |
31 |
Table 3:
DRG labels by number of conjunctions
|
32 |
|
|
|
Count of conjunctions |
[Table 3]
The next graphic shows the total number of DRGs
and the use of conjunctions
within American, Australian and German DRG systems
over time.
The total number of DRGs is displayed by the length of the bars.
The bars are split into fields whose relative sizes
represent the number of DRGs with a count of conjunctions
of 0, 1, 2, . . .
This number of conjunctions is written below the bars.
The number of DRGs with the same count of conjunctions is
shown above the bars.
The fields for DRGs with up to tree conjunctions are coloured in blue.
The fields for DRGs with four or more conjunctions are coloured
in orange and red.
Thus the evolution of the relation of the number of DRGs with less than four
and with four or more conjunctions can be seen at first glance. |
33 |
|
Interpretation:
– Medicare: ± stable
– AR-DRG: ± stable
– G-DRG: ++ increase |
It can be seen, that the lengths of the bars
(and thus the total numbers of DRGs)
remain nearly unchanged for Medicare DRGs and Australian DRGs.
Furthermore, the relative proportions
of the light blue and the orange fields
(thus the numbers of DRGs with three, four conjunctions and more)
remain rather stable with Medicare DRGs
but increase much with German DRGs.
The number of GDRGs with zero, one or two conjunctions
(the total length of the first three fields)
has even decreased since 2004,
although the total number of GDRGs has increased. |
34 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5.2 |
Medicare DRGs (USA)
|
35 |
|
Number of DRGs:
slight increase |
The first DRG system used for remuneration was Medicare DRG 2.0 (1983).
It had 470 DRGs.
Ten years later, the number of groups was still below 500.
The 2007 version encompasses 538 groups.
Thus the increase of the number of Medicare DRGs was rather modest. |
36 |
Table 4:
Examples of Medicare DRG labels with few conjunctions |
37 |
| DRG
| Version
| Conjunctions
| Label
|
| 1
| v23
| 2
| CRANIOTOMY AGE >17 W CC
|
| 9
| v23
| 1
| SPINAL DISORDERS & INJURIES
|
| 20
| v23
| 1
| NERVOUS SYSTEM INFECTION EXCEPT VIRAL MENINGITIS
|
| 193
| v23
| 3
| BILIARY TRACT PROC EXCEPT ONLY CHOLECYST W OR W/O C.D.E. W CC
|
|
|
|
≥ 4 conjunctions: 13 % |
[Table 4]
The quota of labels with four conjunctions or more increased
from 1992 until 2006 from 9 % to 10 %).
Only 13 DRG labels (2.4 %) show five or more conjunctions.
Thus most of the DRG labels use three or fewer conjunctions. |
38 |
|
|
The shift to MS-DRG for 2008
(with the introduction of MCCs) brought a serious change:
The number of DRGs without a conjunction sank from 84 DRGs to 44 DRGs,
whereas the number of DRGs with two conjunctions
increased from 126 to 263,
and the number of DRGs with three conjunctions
increased from 76 to 162.
But because the total number also increased (from 538 to 745 DRGs),
the quota of labels with four conjunctions or more
increased only from 10 % to 13 %. |
39 |
Table 5:
Examples of complex labels of Medicare DRGs |
40 |
| DRG
| Version
| Conjunctions
| Label
|
| 3
| v25
| 7
| ECMO or trach w MV 96+ hrs or PDX exc face, mouth & neck w maj O.R
|
| 541
| v24
| 7
| ECMO OR TRACH W MV 96+HRS OR PDX EXC FACE, MOUTH & NECK W MAJ O.R.
|
| 4
| v25
| 6
| Trach w MV 96+ hrs or PDX exc face, mouth & neck w/o maj O.R
|
| 542
| v24
| 6
| TRACH W MV 96+HRS OR PDX EXC FACE, MOUTH & NECK W/O MAJ O.R.
|
| 563
| v25
| 8
| Fx, sprn, strn & disl except femur, hip, pelvis & thigh w/o MCC
|
| 251
| v24
| 7
| FX, SPRN, STRN & DISL OF FOREARM, HAND, FOOT AGE >17 W/O CC
|
| 494
| v25
| 6
| Lower extrem & humer proc except hip,foot,femur w/o CC/MCC
|
| 219
| v24
| 6
| LOWER EXTREM & HUMER PROC EXCEPT HIP,FOOT,FEMUR AGE >17 W/O CC
|
| 115
| v23
| 5
| PRM CARD PACEM IMPL W AMI/HR/SHOCK OR AICD LEAD OR GNRTR
|
|
|
8
Furthermore, more or less commonly used medical abbreviations
(like "ECMO" for "Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation"
or "FX" for "fracture")
are mixted with arbitrary abbreviations just used
for this special list of DRG labels
(like "TRACH" for "trachestomy",
"SPRN" for "sprain",
"STRN" for "strain",
"DISL" for "dislocation",
"PRM" for "permanent",
"GNRTR" for "generator").
|
|
[Table 5]
(Preliminary remark for Table 5:
When we look at the examples of complex Medicare DRG labels,
we see immediately that an additional problem arises
for people who are not too familiar with medical expressions:
words within long DRG labels are abbreviated until
they are no longer recognizable.8
This problem will not be treated in this paper.) |
41 |
|
|
The most complex DRG label was found
for Medicare DRG 541 (version 24 for 2007).
Eight conjunctions were used (and many abbreviations!).
The full label is:
"ECMO or Tracheostomy
With Mechanical Ventilation 96+ Hours
or Principal Diagnosis Except Face, Mouth and Neck
With Major O.R. Procedure".
(From a purely logical point of view it is not clear
if the "or" of the part
"or Principal Diagnosis Except . . ."
corresponds to the "or" of
"or Tracheostomy"
or to the "With" of
"With Mechanical Ventilation 96+ Hours".
If there is some knowlegde of the matter,
then the question can be decided in favour of the second possibility.) |
42 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5.3 |
AN- and AR-DRGs (Australia)
|
43 |
|
Constant number of DRGs |
The AN-DRG system 3.1 (with 667 DRGs) was used in 1996.
The refined AR-DRG system 4.0 (with 661 DRGs) was introduced in 1998.
The currently used system ARDRG-5.2 encompasses 665 DRGs. |
44 |
Table 6:
Examples of AR-DRG labels with few conjunctions |
45 |
| AR-DRG
| Version
| Conjunctions
| Label
|
| B02A
| v52
| 1
| Craniotomy W Catastrophic CC
|
| B61A
| v52
| 3
| Spinal Cord Conditions W or W/O OR Procedures W Catastrophic or Severe CC
|
| B72B
| v52
| 3
| Nervous System Infection Except Viral Meningitis W/O Cat or Sev CC
|
| H02B
| v52
| 3
| Major Biliary Tract Procedures W/O Malignancy W (Severe or Moderate CC)
|
|
|
|
≥ 4 conjunctions: 13 % |
[Table 6]
The quota of labels with four conjunctions or more changed
from 1996 through 1998 until 2006
from 11 % through 15 % to 13 %.
28 DRG labels (4.2 %) show five or more conjunctions.
Thus many DRG labels use three or fewer conjunctions. |
46 |
Table 7:
Examples of complex labels of AR-DRGs |
47 |
| AR-DRG
| Version
| Conjunctions
| Label
|
| I75B
| v52
| 7
| Injury to Shoulder, Arm, Elbow, Knee, Leg or Ankle Age >64 or W CC
|
| I12C
| v52
| 6
| Infect/Inflam Bone and Joint W Misc Musc Sys and Conn Tiss Proc W/O Cat or Sev CC
|
| H61B
| v52
| 5
| Malignancy of Hepatobiliary Sys,Panc (Age>69 W/O Cat or Sev CC) or W/O Cat CC
|
| P60A
| v52
| 4
| Neonate, Died or Transferred <5 Days of Adm, W/O Significant OR Proc, Newborn
|
| P60B
| v52
| 4
| Neonate, Died or Transferred <5 Days of Adm, W/O Significant OR Proc, Not Newborn
|
| I73B
| v52
| 4
| Aftercare of Musculoskeletal Implants/Prostheses Age >59 or W (Cat or Sev CC)
|
|
|
|
|
[Table 7]
The most complex DRG labels were found for the ARDRGs
belonging to Base AR-DRG I75:
Seven conjunctions were used to define each of these three ARDRGs. |
48 |
|
|
To be able to understand the logical structure of the labels,
logical brackets are used where necessary
(e. g. for ARDRG H02B, H61B and I73B,
shown in the tables above). |
49 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
5.4 |
G-DRGs (Germany)
|
50 |
|
Strongly increasing number of DRGs |
While the G-DRG system started with
661
DRGs for the year 2003;
the G-DRG system 2008 has arrived at
1137
DRGs. |
51 |
Table 8:
Examples of G-DRG labels with few conjunctions |
52 |
| G-DRG
| Vers.
| Conj.
| Label (translated)
| Label (original)
|
| B73Z
| 2008
| 0
| Viral Meningitis
| Virusmeningitis
|
| I11Z
| 2008
| 0
| Limb Lengthening Procedures
| Eingriffe zur Verlängerung einer Extremität
|
|
|
|
≥ 4 conjunctions:
49 % |
[Table 8]
The quota of labels with four or more conjunctions increased
from 2003 until 2008
from 17 %
to 49 %.
367
G-DRG labels
(32 %)
show five or more conjunctions.
Thus nearly half of all DRG labels use four or more conjunctions,
and nearly one third use five or more! |
53 |
|
Example: G-DRG B02B |
I will take B02B
as a first example of a complex G-DRG label.
Word-by-word translations are made by the author
(with commas set according to the German original). |
54 |
Table 9:
History of labels for G-DRG B02B |
55 |
| G-DRG
| Vers.
| Conj.
| Label (translated)
| Label (original)
|
| B02B
| 2008
| 10
| Complex Craniotomy
or Spinal Procedure
or Other Expensive Nervous System Procedure
With Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours,
Without Radiotherapy More Than 8 Sessions,
Age < 6 Years
or Age < 18 Years
With Major Intracranial Procedure,
With Catastrophic CC
or Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours
and Motor Ventilation Under 178 Hours
| Komplexe Kraniotomie
oder Wirbelsäulen-Operation
od. andere aufwändige Operation am Nervensystem
mit Beatm. > 95 Std.,
ohne Strahlenth. > 8 Bestrahl.,
Alter < 6 J.
od. < 18 J.
mit großem intrakr. Eingr.,
m. äußerst schw. CC
od. Beatm. > 95
und < 178 Std.
|
| B02B
| 2007
| 9
| Complex Craniotomy
or Spinal Procedure
or Other Expensive Nervous System Procedure
With Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours,
Without Radiotherapy More Than 8 Sessions,
Age < 6 Years
or Age < 18 Years
With Major Intracranial Procedure,
With Catastrophic CC
or Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours
| Komplexe Kraniotomie
oder Wirbelsäulen-Operation
od. andere aufwändige Operation am Nervensystem
mit Beatmung > 95 Std.,
ohne Strahlenth. mehr als 8 Bestrahl.,
Alter < 6 J.
od. < 18 J.
mit großem intrakran. Eingr.,
m. äußerst schw. CC
od. Beatm. > 95 Std.
|
| B02B
| 2006
| 7
| Complex Craniotomy
or Spinal Procedure
or Other Expensive Nervous System Procedure
With Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours,
Without Radiotherapy More Than 8 Sessions,
Age < 6 Years
or Age < 18 Years
With Major Intracranial Procedure
| Komplexe Kraniotomie
oder Wirbelsäulen-Operation
oder andere aufwändige Operation am Nervensystem
mit Beatmung > 95 Stunden,
ohne Strahlentherapie mehr als 8 Bestrahlungen,
Alter < 6 Jahre
oder Alter < 18 Jahre
mit grossem intrakraniellen Eingriff
|
| B02B
| 2005
| 4
| Craniotomy
or Complex Spinal Procedure
Without Early Rehabilitation
With Radiotherapy More Than 8 Sessions
| Kraniotomie
oder komplexe Wirbelsäulen-OP
ohne Frührehabilitation,
mit Strahlentherapie, mehr als 8 Bestrahlungen
|
| B02B
| 2004
| 4
| Craniotomy
With Catastrophic CC
or Epilepsy Surgery,
Without Early Rehabilitation
and Complex Geriatric Treatment
| Kraniotomie
mit äusserst schweren CC
oder Epilepsiechirurgie,
ohne Frührehabilitation
und Geriatrische Komplexbehandlung
|
| B02B
| 2003
| 2
| Craniotomy
With Severe
or Moderate CC
| Kraniotomie
mit schweren
oder mässigen CC
|
|
|
9
In the G-DRG manual you will find the following entry
as definiton for the base GDRG-2007 B02:
«(
mindestens eine Prozedur aus den Tabellen
TAB-B02-1, TAB-B02-2
und (PCCL > 3 oder Dauer der
maschinellen Beatmung > 95 Stunden oder mindestens eine
Prozedur aus den Tabellen TAB-B02-3, TAB-B02-4)
oder Prozedur in Tabelle TAB-B02-5
oder (mindestens eine
Prozedur aus den Tabellen TAB-B02-6, TAB-B02-7 oder
mindestens eine Prozedur aus den Tabellen TAB-B02-8,
TAB-B02-9, TAB-B02-10, TAB-B02-11 und PCCL > 3)
und Dauer
der maschinellen Beatmung > 95 Stunden
)und(
mindestens eine Prozedur aus den Tabellen TAB-B02-3, TAB-B02-12
oder PCCL > 3
oder Dauer der maschinellen Beatmung >
95 Stunden
oder Komplizierende Prozeduren
oder Prozedur in Tabelle TAB-B02-13
)» [in the original no broken lines and no emphasising]
and as additional definition for the split of B02B:
«(
Alter < 6 Jahre oder Alter < 18 Jahre
und Prozedur in Tabelle TAB-B02-4
) und (
PCCL > 3
oder Dauer der maschinellen Beatmung > 95 Stunden
)».
Thus it becomes evident that motor ventilation
is repeated because it is a condition of the base DRG
which not always must be present,
and it is also a condition within the split condition
which not always must be present.
And it becomes also evident that it is nearly impossible
to resume such a complicated logical expression in a
«short» expression which should be usable as a G-DRG name.
10
Bartkowski et al. [G-DRG 2006, 2006]: B02–1.
|
|
[Table 9]
In the 2007 version this G-DRG
is described with the use of nine conjunctions.
(Although the resulting label is very complicated,
there are G-DRG labels with even more conjunctions!)
We can first see a list of three groups of procedures
(complex craniotomy;
spinal procedures;
other expensive nervous procedures).
Then three conditions are added
(with motor ventilation over 95 hours;
without radiotherapy with more than eight sessions;
with age < 6 years).
What follows is rather unclear.
I interpret it as an alternative age limit
(age < 18 years):
if this limit is fullfilled, the next two conditions
have to be coded
(with major intracranial procedure;
with catastrophic CC).
But now, the question will arise:
why is motor ventilation named a second time?
Is there another logic than the one described above?
Is it not correct to think in terms of a second, age-dependent branch?9
If one reads Bartkowski et al.10
one is astonished once more:
he says that according to his analyses,
the motor ventilation split
does not have any relevance in this DRG because
cases with such ventilations will be assigned
to one of the Pre-MDC Base GDRGs (A06 to A13). |
56 |
|
|
When compared with the G-DRG label in the sequence of the years
since 2003,
one sees
how the texts have grown,
how the conjunctions have been multiplying,
how it takes more and more effort
to decipher the meaning. |
57 |
|
|
[Table 10]
Seen in the context of the other DRGs of Base DRG B02,
it becomes a challenge to find out the real differences
between these DRGs
in such a manner that one is able to explain them to
someone else (and there will be hardly a difference if
he is a clinician or a manager). |
58 |
Table 10:
Examples of complex labels of G-DRGs: Base-DRG B02 |
59 |
| G-DRG
| Vers.
| Conj.
| Label (translated)
| Label (original)
|
| B02A
| 2007
| 5
| Complex Craniotomy
or Spinal Procedure
or Other Expensive Nervous System Procedure
With Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours,
With Radiotherapy More Than 8 Sessions
| Komplexe Kraniotomie
oder Wirbelsäulen-Operation
oder andere aufwändige Operation am Nervensystem
mit Beatmung > 95 Stunden,
mit Strahlentherapie, mehr als 8 Bestrahlungen
|
| B02B
| 2007
| 9
| Complex Craniotomy
or Spinal Procedure
or Other Expensive Nervous System Procedure
With Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours,
Without Radiotherapy More Than 8 Sessions,
Age < 6 Years
or Age < 18 Years
With Major Intracranial Procedure,
With Catastrophic CC
or Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours
| Komplexe Kraniotomie
oder Wirbelsäulen-Operation
od. andere aufwändige Operation am Nervensystem
mit Beatmung > 95 Std.,
ohne Strahlenth. mehr als 8 Bestrahl.,
Alter < 6 J.
od. < 18 J.
mit großem intrakran. Eingr.,
m. äußerst schw. CC
od. Beatm. > 95 Std.
|
| B02C
| 2007
| 5
| Complex Craniotomy
or Spinal Procedure
or Other Expensive Nervous System Procedure
With Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours,
With Radiotherapy Less Than 9 Sessions
| Komplexe Kraniotomie
oder Wirbelsäulen-Operation
oder andere aufwändige Operation am Nervensystem
mit Beatmung > 95 Stunden,
mit Strahlentherapie, weniger als 9 Bestrahlungen
|
| B02D
| 2007
| 8
| Complex Craniotomy
or Spinal Procedure
or Other Expensive Nervous System Procedure
With Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours,
Without Radiotherapy,
With Complicating Procedures
or Major Intracranial Procedure
Without Catastrophic CC,
Without Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours
| Komplexe Kraniotomie
oder Wirbelsäulen-Operation
oder andere aufwändige Operation am Nervensystem
mit Beatmung > 95 Stunden,
ohne Strahlentherapie,
mit komplizierenden Prozeduren
oder großem intrakran. Eingr.
ohne äußerst schw. CC,
ohne Beatmung > 95 Std.
|
| B02E
| 2007
| 7
| Complex Craniotomy
or Spinal Procedure
or Other Expensive Nervous System Procedure
With Motor Ventilation Over 95 Hours,
Without Radiotherapy,
Age > 5 Years,
Without Major Intracranial Procedure,
Without Complicating Procedures
| Komplexe Kraniotomie
oder Wirbelsäulen-Operation
oder andere aufwändige Operation am Nervensystem
mit Beatmung > 95 Stunden,
ohne Strahlentherapie,
Alter > 5 Jahre,
ohne großen intrakraniellen Eingriff,
ohne komplizierende Prozeduren
|
|
|
|
Example: Base G-DRG R60 |
[Table 11]
A second example:
the Leukaemia Base G-DRG R60 is differentiated
into seven GDRGs (R60A until RA60G)
according to severity of illness and intensity of treatment.
A look at the label list shows
that there are rather easily understandable
labels with three or fewer conjunctions.
But others have nine or ten conjunctions.
It is rather hard to understand their meaning by reading them only once. |
60 |
Table 11:
Examples of complex labels of G-DRGs: Base-DRG R60 |
61 |
| G-DRG
| Vers.
| Conj.
| Label (translated)
| Label (original)
|
| R60A
| 2008
| 1
| Acute Myeloic Leukaemia
With Extremly Complex Chemotherapy
| Akute myeloische Leukämie
mit hochkomplexer Chemotherapie
|
| R60B
| 2008
| 4
| Acute Myeloic Leukaemia
With Intensive Chemotherapy
With Complicating Diagnosis
or Dialysis
or Port Implantation
| Akute myeloische Leukämie
mit intensiver Chemotherapie
mit komplizierender Diagnose
oder Dialyse
oder Portimplantation
|
| R60C
| 2008
| 9
| Acute Myeloic Leukaemia
With Intensive Chemotherapy
Without Complicating Diagnosis,
Without Dialysis,
Without Port Implantation,
With Catastrophic CC
or With Moderatly Complex Chemotherapy
With Complicating Diagnosis
or Dialysis
or Port Implantation
| Akute myeloische Leukämie
mit intensiver Chemotherapie
ohne komplizierende Diagnose,
ohne Dialyse,
ohne Portimplantation,
mit äußerst schweren CC
oder mit mäßig komplexer Chemotherapie
mit komplizierender Diagnose
oder Dialyse
oder Portimplantation
|
| R60D
| 2008
| 10
| Acute Myeloic Leukaemia
With Intensive Chemotherapy
Without Complicating Diagnosis,
Dialysis
or Port Implantation,
Without Catastrophic CC
or With Moderatly Complex Chemotherapy
With Catastrophic CC
or With Dialysis
or Catastrophic CC,
Age < 16 Years
| Akute myeloische Leukämie
mit intensiver Chemotherapie
ohne komplizierende Diagnose,
Dialyse
oder Portimplant.,
ohne äußerst schwere CC
oder mit mäßig komplexer Chemoth.
mit äußerst schweren CC
oder mit Dialyse
oder äußerst schweren CC,
Alter < 16 Jahre
|
| R60E
| 2008
| 3
| Acute Myeloic Leukaemia
With Dialysis
or Catastrophic CC,
Age > 15 Years
| Akute myeloische Leukämie
mit Dialyse
oder äußerst schweren CC,
Alter > 15 Jahre
|
| R60F
| 2008
| 6
| Acute Myeloic Leukaemia
With Moderatly Complex Chemotherapy,
Without Complicating Diagnosis,
Without Dialysis,
Without Port Implantation,
Without Catastrophic CC
or With Locale Chemotherapy
| Akute myeloische Leukämie
mit mäßig komplexer Chemotherapie,
ohne komplizierende Diagnose,
ohne Dialyse,
ohne Portimplantation,
ohne äußerst schwere CC
oder mit lokaler Chemotherapie
|
| R60G
| 2008
| 3
| Acute Myeloic Leukaemia
Without Chemotherapy,
Without Dialysis,
Without Catastrophic CC
| Akute myeloische Leukämie
ohne Chemotherapie,
ohne Dialyse,
ohne äußerst schwere CC
|
|
|
11
Upper und lower letters show different hierarchical levels
of the corresponding terms.
–
An addition remark:
What is the order of the types of chemotherapy like:
extremely complex / moderately complex / intensive / local,
or:
extremely complex / intensive / moderately complex / local?
The latter is used by
Bartkowski et al. [G-DRG 2006, 2006]: R60–1
and it could be derived from the order in the label of R60C;
the former looks like the intuitively logical form.
|
|
[Table 12]
To understand the labels better, they were subjected to a logical analsis.
A certain system could be recognised throughout the DRGs of this Base G-DRG,
yet I am still unable to assign quickly
a patient which belongs to Base G-DRG R60,
to the correct G-DRG.11 |
62 |
Table 12:
GDRG-2008: Analysis of the logical structure of Base G-DRG R06 |
| Term
| R60A
| R60B
| R60C
| R60D
| R60E
| R60F
| R60G
|
| Acute Myeloic Leukaemia
| X
| X
| X
| X
| X
| X
| X
|
| (and)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - (either) With Extremely Complex Chemoth.
| X
| -
| -
| -
| -
| -
| /
|
| - (or) With Intensive Chemotherapy
| -
| X
| O
| O
| -
| -
| /
|
| - - (and)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - - - (or) With Complicating Diagnosis
| .
| o
| /
| /
| .
| .
| .
|
| - - - (or) Dialysis
| .
| o
| /
| /
| .
| .
| .
|
| - - - (or) Port Implantation
| .
| o
| /
| /
| .
| .
| .
|
| - - (and) With Catastrophic CC
| .
| .
| x
| /
| .
| .
| .
|
| - (or) With Moderately Complex Chemoth.
| -
| -
| O
| O
| -
| O
| /
|
| - - (and)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - - - (or) With Complicating Diagnosis
| .
| .
| o
| -
| .
| /
| .
|
| - - - (or) Dialysis
| .
| .
| o
| -
| .
| /
| .
|
| - - - (or) Port Implantation
| .
| .
| o
| -
| .
| /
| .
|
| - - (and) With Catastrophic CC
| .
| .
| .
| x
| .
| /
| .
|
| - (or) With Locale Chemotherapy
| -
| -
| -
| -
| -
| O
| /
|
| - (or) With Dialysis
| -
| -
| -
| O
| O
| -
| /
|
| - (or) Catastrophic CC
| -
| -
| -
| O
| O
| -
| /
|
| (and) Age < 16 Years
| -
| -
| -
| X
| /
| -
| -
|
|
63 |
|
Additional examples |
[Table 13]
The last table shows that the above two examples are not rare cases,
but that there is a rather long list of GDRGs
which use many conjunctions and which are therefore hard to understand. |
64 |
Table 13:
Additional examples of complex labels of G-DRGs |
65 |
| G-DRG
| Version
| Conjunctions
| Label
|
| A09A
| 2008
| 10
| Beatmung > 499 und < 1000 Stunden mit komplexer OR-Prozedur oder Polytrauma und hochkomplexem Eingriff oder Alter < 16 Jahre oder ohne komplexe OR-Prozedur, ohne Polytrauma, mit angeborener Fehlbildung oder Tumorerkrankung, Alter < 3 Jahre
|
| A13A
| 2008
| 9
| Beatmung > 95 und < 250 Stunden mit hochkomplexem Eingriff oder intensivmedizinischer Komplexbehandlung > 1656 Punkte oder > 1105 Punkte mit komplexer OR-Prozedur oder komplizierenden Prozeduren und bestimmter OR-Prozedur oder bei Lymphom und Leukämie
|
| B03Z
| 2008
| 11
| Operative Eingriffe bei nicht akuter Para- / Tetraplegie oder Eingriffe an Wirbelsäule und Rückenmark bei bösartiger Neubildung od. mit äusserst schweren od. schw. CC oder Eingriffe b. zerebraler Lähmung, Muskeldystrophie, Neuropathie mit äusserst schw. CC
|
| B17A
| 2008
| 12
| Eingriffe an peripheren Nerven, Hirnnerven und anderen Teilen des Nervensyst. ohne äusserst schw. CC, ohne kompliz. Diag. oder Eingr. bei zerebr. Lähmung, Muskeldystrophie od. Neuropathie ohne äusserst schw. od. schw. CC, Alter > 18 J., mit komplexer Diag.
|
| B69C
| 2008
| 6
| Transitorische ischämische Attacke (TIA) und extrakranielle Gefässverschlüsse mit äusserst schweren CC, ohne neurologische Komplexbehandlung des akuten Schlaganfalls oder Demenz und andere chronische Störungen der Hirnfunktion
|
| B70A
| 2008
| 9
| Apoplexie oder Transitorische ischämische Attacke (TIA) und extrakranielle Gefässverschlüsse mit Beatmung > 95 und < 178 Stunden oder Apoplexie mit intrakranieller Blutung und neurologischer Komplexbehandlung des akuten Schlaganfalls, mehr als 72 Stunden
|
| B71C
| 2008
| 13
| Erkrankungen an Hirnnerven und peripheren Nerven mit komplexer Diagnose, ausser bei Para- / Tetraplegie, ohne schwere CC oder ohne komplexe Diagnose, mit äusserst schweren od. schweren CC ausser bei Para- / Tetrapl. oder ohne schwere CC bei Para- / Tetrapl.
|
| E69E
| 2008
| 10
| Bronchitis und Asthma bronchiale, Alter > 5 Jahre und < 16 Jahre, ein Belegungstag oder ohne äusserst schwere oder schwere CC oder Beschwerden und Symptome der Atmung ohne komplexe Diagnose, Alter < 16 Jahre
|
| F24C
| 2008
| 14
| Impl. Herzschrittm., 2-Kammersyst. ohne kompl. Eingr. oder PTCA mit kompl. Diagn. und hochkompl. Intervent. od. mit PTA, ohne äusserst schw. CC, Alter > 15 J. oder Revision Herzschrittm. od. Kardioverter/Defibr. (AICD) ohne Aggregatwechsel, Alter < 16 J.
|
| G24Z
| 2008
| 13
| Eingriffe bei Bauchwandhernien, Nabelhernien und anderen Hernien, Alter > 0 Jahre oder beidseitige Eingriffe bei Leisten- und Schenkelhernien, Alter > 0 Jahre und < 56 Jahre oder Eingriffe bei Leisten- und Schenkelhernien, Alter > 55 Jahre
|
| G67B
| 2008
| 14
| Ösophagitis, Gastroenteritis u. versch. Erkr. d. Verdauungsorg. m. kompl. Diag. od. Alter <1 J. od. gastroint. Blutung, m. äuss. schw. od. schw. CC od. Alt. >74 J. od. Ulkuserkr. m. schw. CC od. Alt. >74 J., >1 Beleg.tag, ohne kompliz. Diag., ohne Dialyse
|
| I75B
| 2008
| 11
| Schwere Verletzungen von Schulter, Arm, Ellenbogen, Knie, Bein und Sprunggelenk ohne CC oder Entzündungen von Sehnen, Muskeln und Schleimbeuteln ohne äusserst schwere oder schwere CC
|
| L64A
| 2008
| 10
| Harnsteine und Harnwegsobstruktion, Alter > 75 Jahre od. mit äusserst schweren oder schweren CC oder Urethrastriktur, andere leichte bis moderate Erkr. der Harnorgane, mehr als ein Beleg.tag oder Beschw. und Symptome der Harnorgane oder Urethrozystoskopie
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
6 |
Discussion
|
66 |
|
|
We have seen that the use of conjunctions impairs the comprehensibility
of DRG labels.
The effort required to ascertain
the meaning of a logically complex DRG label
can be rather great. |
67 |
|
Method chosen
was a simple one |
The method chosen was a simple one.
It can be criticised that not all conjunctions used
for the analysis have the same impact on comprehensibility.
For instance, the use of commas is easier to understand than a
sequence of and's and or's.
Yet it was helpful to detect quite an interesting set
of problematic DRG labels. |
68 |
|
|
The conjunctions "more", "less",
"<", ">" were not counted
because their relation to the previous words is always
strong and the following words (a number and a
unit) are much easier to understand than clinical terms. |
69 |
12
An example of this case is GDRG-2007 B69C:
"Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) and Extracranial Vascular Occlusion With Catastrophic CC, Without Neurological Complex Treatment Of Acute Myocardial Infarction or Dementia and Other Chronic Cerebral Disorders".
(The original label was:
"Transitorische ischämische Attacke (TIA) und extrakranielle Gefässverschlüsse mit äusserst schweren CC, ohne neurologische Komplexbehandlung des akuten Schlaganfalls oder Demenz und andere chronische Störungen der Hirnfunktion".)
13
The label of Medicare DRG 541 version 23 is:
"ECMO or Tracheostomy
With Mechanical Ventilation 96+ Hours
or Principal Diagnosis Except Face, Mouth and Neck
With Major O.R. Procedure".
Which other part or parts of the label
is
the term
"or Principal Diagnosis"
related to? (Ventilation? Tracheostomy? ECMO or Tracheostomy?)
–
GDRG-2007 P67D is
another example of this type:
"Newborn, Admission Weight > 2499 g Without Significant O.R. Procedure, Without Mechanical Ventilation > 95 Hours, Without Another Problem or Without a Severe Problem, Sameday".
(The original label was:
"Neugeborenes, Aufnahmegewicht > 2499 g ohne signifikante OR-Prozedur, ohne Beatmung > 95 Stunden, ohne anderes Problem oder ohne schweres Problem, ein Belegungstag".)
Which other part or parts of the label
is
the term
"sameday" related to?
(Is this G-DRG only assigned to sameday patients?
Or is "sameday" related to one or
some terms of the list of exclusions?
– One has to know
and study the labels of P67C and P67B to be able
to guess the right meaning.)
14
An example of this case is GDRG-2007 B71C:
"Cranial and Peripheral Nerve Disorders With Complex Diagnosis, Except With Para-/Quadriplegia, Without Severe CC or Without Complex Diagnosis, With Catastrophic or Severe CC Except With Para-/Quadriplegia or Without Severe CC With Para-/Quadriplegia".
(The original label was:
"Erkrankungen an Hirnnerven und peripheren Nerven mit komplexer Diagnose, ausser bei Para- / Tetraplegie, ohne schwere CC oder ohne komplexe Diagnose, mit äusserst schweren oder schweren CC ausser bei Para- / Tetrapl. oder ohne schwere CC bei Para- / Tetrapl.".)
15
An example of this case is GDRG-2007 G07B:
"Appendectomy With Peritonitis With Catastrophic or Severe CC or Minor Small Intestine and Colon Procedures Without Catastrophic CC, Age > 2 Years".
(The original label was:
"Appendektomie bei Peritonitis mit äusserst schweren oder schweren CC oder kleine Eingriffe an Dünn- und Dickdarm ohne äusserst schwere CC, Alter > 2 Jahre".)
|
Logical problems |
The overuse of conjunctions led to the following types of problems:
-
The logic of sequences of commas,
and's and or's
is not anymore immediately comprehensible.12
-
The logic can become ambiguous.13
-
The logic can even lead to practically unintellegible labels.14
-
Usability is impaired by concatenating different clinical contents
which are expected to have the same costs,
into a single DRG.15
|
70 |
16
Examples of this case are: Medicare DRG 509 version 23:
"Full Thickness Burn
W/O Skin Grft or Inh Inj W/O CC or Sig Trauma",
or ARDRG-5.2 I12C:
"Infect/Inflam Bone and Joint W Misc Musc Sys and Conn Tiss Proc W/O Cat or Sev CC".
17
An example of this case is ARDRG-5.2 G44C:
"Other Colonoscopy, Sameday":
The term "sameday" is not used in G44A and G44B:
G44A: "Other Colonoscopy W Catastrophic or Severe CC".
G44B: "Other Colonoscopy W/O Catastrophic or Severe CC".
18
For instance GDRG-2007 A13A: "Beatmung > 95 und < 250 Stunden mit hochkomplexem Eingriff oder intensivmedizinischer Komplexbehandlung > 1104 Punkte oder mit bestimmter OR-Prozedur und komplizierenden Prozeduren, mit intensivmedizinischer Komplexbehandlung > 1104 Punkte".
19
For instance ARDRG-5.2 H06Z: "Other Hepatobiliary and Pancreas OR Procedures"
(identical with GDRG-2007 H06Z:
"Andere OR-Prozeduren an hepatobiliärem System und Pankreas"),
or: GDRG-2007 I44C: "Various Knee Endoprothesis Procedures"
(original label:
"Verschiedene Endoprotheseneingriffe am Kniegelenk").
20
For instance GDRGs-2007
B17A, B17B, B17C and B07Z concern
"Peripheral and Cranial Nerve and
Other Nervous System Procedures".
GDRGs B17A, B17B, B17C, B06A, B06B, B03Z concern
"Procedures for Cerebral Palsy,
Muscular Dystrophy, Neuropathy".
The problem lies in the fact that the themes of the Base GDRGs
B07 and B06 and parts of B03
are put together in B17 by the use of the conjunction "or".
|
Other problems |
Other techniques which generate
not easily understandable labels are:
-
The creation and use of new and special abbreviations.16
-
The use of differentiating terms in only a part
of all DRGs of a Base DRG.17
-
The use of container words like
"certain OR procedures".18
-
The overuse of "hotchpotch" DRGs: DRGs for "other"
diagnoses.19
-
The distribution of DRGs which belong to one single Base DRG,
into several Base DRGs.20
|
71 |
21
To get more transparency,
one could define two level DRG systems:
the first level would consist of "clinical DRGs".
On the second level, these could be collapsed into
"economical DRGs".
The latter would have similar costs but
it would be accepted that they are
not too strictly clinically homogenous.
–
An example of a two level system (of rehabilition patient categories)
are the TAR-FIM classes in conjunction with the nursing cost categories
of the TAR system.
Cf. Fischer et al. [TAR und Reha-PCS, 2006]: 18 ff.
22
Such a system is used by the Austrian LDFs
("Leistungsbezogene Diagnosen-Fallgruppen").
23
This was realised e. g.
with LDF (partially), Disease Staging, SQLape,
HRG4 (partially: "unbundled HRGs").
|
Better DRG labels? |
To get better DRG labels, it could be of help:
-
To use logical brackets (as it was done in the AR-DRG system).
-
To split up complex DRGs for clinical homogeneity.21
-
To construct patient classification systems for the use
within "cushioned" remuneration systems.
(For instance: define for each DRG combined per diem and per case rates22
or create systems
in which more than one group can be assigned to each case.23)
|
72 |
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
7 |
Conclusion
|
73 |
|
|
A DRG system should not only be useful for statisticians,
but it should also serve
as a basis for discussions between clinicians and managers.
Thus it is necessary to make sure that DRG labels are compehensible.
This is especially important when DRG systems are strongly optimised
with regard to statistical performance
(as it was done with the G-DRG system). |
74 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|^·<×>·v| |
8 |
References
|
75 |
|
-
Bartkowski et al.
- G-DRG 2006
2006
| Bartkowski R, Bauer H, Witte J. G-DRG. Praxiskommentar zum Deutschen Fallpauschalen-System. Mit 3. Ergänzungslieferung, Landsberg (Ecomed) 2006. | 76 |
|
-
Fetter et al.
- DRGs
1991
| Fetter RB, Brand A, Dianne G [Hrsg.]. DRGs, Their Design and Development. Ann Arbor (Health Administration Press) 1991: 341 pp. | 77 |
|
-
Fischer
- PCS
1997
| Fischer W. Patientenklassifikationssysteme zur Bildung von Behandlungsfallgruppen im stationären Bereich. Prinzipien und Beispiele. Bern und Wolfertswil (ZIM) 1997: 514 pp. Auszüge:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / studien / PCS-Buch-9701-Info.htm. | 78 |
|
-
Fischer et al.
- TAR und Reha-PCS
2006
| Fischer W, Blanco J, Mäder M, Zangger P, Conti FM, et al.. Das TAR-System und andere Patientenklassifikationssysteme für die Rehabilitation. TAR-Forschungsbericht und Kurzbeschrieb von Systemen aus Deutschland, Frankreich, Australien und den USA. Wolfertswil (ZIM) 2006: 89 pp. Info:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / studien / TAR-RehaPCS-0607-Info.htm. | 79 |
|
-
Fischer
- GDRG-Verständlichkeit
2007
| Fischer W. Sprechen Sie G-DRG?. G-DRG 2007: Statistische Optimierung zu Lasten fachsprachlicher Verständlichkeit. In: Streiflicht Z I M 2007(15)1. Internet:
http:// www.fischer-zim.ch / streiflicht / GDRG-2007-Sprache-0701.htm. | 80 |
![[print]](../PIC/e-div/print.gif)
![[pdf icon]](../PIC/e-div/pdf.gif) pdf file
(100 KB)
pdf file
(100 KB) deutsch
deutsch français
français english
english esperanto
esperanto G-DRG-2007-Verständlichkeit
G-DRG-2007-Verständlichkeit